Navigating the Future: Key Trends Shaping the World in 2025
Related Articles: Navigating the Future: Key Trends Shaping the World in 2025
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Future: Key Trends Shaping the World in 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Future: Key Trends Shaping the World in 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Future: Key Trends Shaping the World in 2025
- 3.1 1. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 3.2 2. The Metaverse: A New Frontier of Digital Interaction
- 3.3 3. The Rise of Sustainable Technologies
- 3.4 4. The Future of Work: Remote Work and Automation
- 3.5 5. The Democratization of Technology
- 3.6 6. The Rise of Personalized Medicine
- 3.7 7. The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity
- 3.8 8. The Rise of the Sharing Economy
- 3.9 FAQs about New Trends in 2025
- 3.10 Tips for Navigating the New Trends in 2025
- 3.11 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Future: Key Trends Shaping the World in 2025
The year 2025 is rapidly approaching, bringing with it a wave of technological advancements, societal shifts, and evolving consumer behavior. Understanding the new trends shaping this landscape is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers alike, as it allows for proactive adaptation and strategic planning. This comprehensive analysis explores eight key new trends that will define the world in 2025, examining their implications and providing insights into how to navigate this evolving landscape.
1. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI has already revolutionized various industries, and its impact is set to intensify in the coming years. Advancements in machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing are enabling AI to perform increasingly complex tasks, from automating mundane processes to generating creative content.
Implications:
- Increased Automation: AI will automate numerous tasks, potentially displacing some jobs while creating new opportunities in AI-related fields.
- Personalized Experiences: AI-powered personalization will enhance customer experiences across various sectors, from e-commerce to healthcare.
- Enhanced Decision Making: AI can analyze vast datasets and provide data-driven insights to inform strategic decisions in business, finance, and government.
Benefits:
- Improved Efficiency: AI automation can streamline processes, reducing costs and increasing productivity.
- Enhanced Innovation: AI can assist in research and development, leading to breakthroughs in various fields.
- Personalized Solutions: AI can tailor products and services to individual needs, improving customer satisfaction.
Examples:
- AI-powered chatbots: Providing customer support and answering inquiries.
- AI-driven medical diagnostics: Assisting physicians in identifying diseases and recommending treatments.
- AI-generated content: Creating personalized marketing campaigns and engaging social media posts.
2. The Metaverse: A New Frontier of Digital Interaction
The metaverse, a persistent, shared virtual world, is emerging as a transformative technology with the potential to revolutionize how we work, socialize, and consume entertainment. This immersive digital space will enable users to interact with each other and digital objects in real-time, blurring the lines between the physical and virtual realms.
Implications:
- Enhanced Social Interactions: The metaverse will provide new avenues for social connection, fostering virtual communities and expanding social networks.
- New Economic Opportunities: The metaverse will create new business models and opportunities for entrepreneurs, artists, and content creators.
- Transformative Education and Training: Immersive learning experiences in the metaverse can revolutionize education and training, providing engaging and interactive environments.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Connectivity: The metaverse can connect people across geographic boundaries, fostering global collaboration and communication.
- Immersive Experiences: The metaverse offers a new level of engagement and immersion, enhancing entertainment, gaming, and social interactions.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: The metaverse can provide equal access to opportunities and experiences for individuals with disabilities or those facing physical limitations.
Examples:
- Virtual concerts and events: Allowing users to attend events from anywhere in the world.
- Virtual offices and workplaces: Enabling remote collaboration and team building in a shared virtual space.
- Virtual shopping and retail experiences: Providing interactive and personalized shopping experiences.
3. The Rise of Sustainable Technologies
As environmental concerns escalate, sustainable technologies are gaining prominence. These technologies focus on reducing carbon emissions, conserving resources, and mitigating the negative impacts of human activities on the planet.
Implications:
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: Consumers are increasingly seeking sustainable products and services, driving demand for eco-friendly solutions.
- Regulatory Changes: Governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations to promote sustainability and reduce environmental impact.
- Business Innovation: Companies are investing in sustainable technologies to reduce their environmental footprint and gain a competitive advantage.
Benefits:
- Environmental Protection: Sustainable technologies help mitigate climate change, conserve resources, and protect biodiversity.
- Economic Growth: Investing in sustainable technologies can create new industries, jobs, and economic opportunities.
- Social Responsibility: Sustainable practices demonstrate corporate responsibility and contribute to a healthier planet for future generations.
Examples:
- Renewable energy sources: Solar, wind, and hydro power generation.
- Electric vehicles: Reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting cleaner transportation.
- Circular economy models: Reusing and recycling materials to reduce waste and minimize resource consumption.
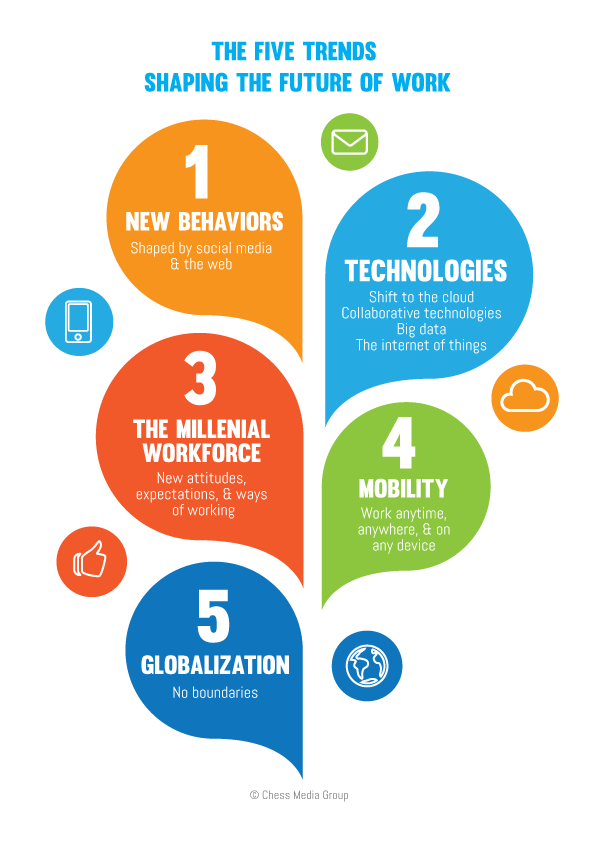
4. The Future of Work: Remote Work and Automation
The pandemic accelerated the shift towards remote work, and this trend is expected to continue in the coming years. Automation is also transforming the workplace, automating repetitive tasks and creating new opportunities for human workers to focus on higher-level skills.
Implications:
- Increased Flexibility: Remote work allows for greater flexibility and work-life balance, attracting talent from diverse locations.
- Redefined Workplace: The traditional office environment is evolving, with a focus on collaboration spaces and hybrid work models.
- Upskilling and Reskilling: Workers will need to adapt to the changing demands of the workforce, acquiring new skills in areas like data analysis, AI, and cybersecurity.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Productivity: Remote work can improve productivity by reducing distractions and allowing for flexible work schedules.
- Reduced Costs: Remote work can reduce overhead costs associated with office space and commuting.
- Increased Diversity and Inclusion: Remote work allows for greater diversity and inclusivity, attracting talent from underrepresented communities.
Examples:
- Remote work platforms: Tools like Zoom, Slack, and Microsoft Teams enable virtual collaboration and communication.
- Automation software: AI-powered tools automate tasks like data entry, scheduling, and customer service.
- Online learning platforms: Providing access to training programs and upskilling opportunities for workers.
5. The Democratization of Technology
Technology is becoming increasingly accessible and affordable, empowering individuals and communities worldwide. This democratization of technology is driving innovation and fostering economic growth in developing countries.
Implications:
- Increased Access to Information: Individuals have access to vast amounts of information and knowledge, enabling them to learn, connect, and participate in global conversations.
- Empowerment and Innovation: Technology empowers individuals and communities to create, innovate, and solve problems, fostering entrepreneurship and social change.
- Bridging the Digital Divide: Technology is playing a crucial role in bridging the digital divide, connecting remote communities and providing access to essential services.
Benefits:
- Economic Development: The democratization of technology fosters innovation and entrepreneurship, driving economic growth and creating new jobs.
- Social Progress: Technology can improve access to education, healthcare, and financial services, promoting social inclusion and equality.
- Global Collaboration: Technology enables individuals and communities to connect and collaborate across borders, fostering international understanding and cooperation.
Examples:
- Open-source software: Providing access to free and customizable software tools.
- Mobile devices and internet connectivity: Expanding access to information and digital services in developing countries.
- Crowdfunding platforms: Enabling individuals to raise funds for projects and initiatives.
6. The Rise of Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine, tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup and lifestyle, is transforming healthcare by providing more effective and targeted treatments. This approach leverages advancements in genomics, bioinformatics, and AI to deliver personalized healthcare solutions.
Implications:
- Precision Diagnostics: Personalized medicine enables earlier and more accurate diagnoses, leading to more effective treatments.
- Targeted Therapies: Treatments can be tailored to individual patients, increasing efficacy and reducing side effects.
- Proactive Healthcare: Personalized medicine allows for preventative measures and early interventions, promoting better health outcomes.
Benefits:
- Improved Patient Outcomes: Personalized medicine leads to better treatment outcomes, reducing hospital readmissions and improving overall health.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: By targeting treatments and preventing complications, personalized medicine can reduce overall healthcare costs.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: Personalized medicine empowers patients to actively participate in their healthcare decisions, leading to better adherence to treatment plans.
Examples:
- Genetic testing: Identifying genetic predispositions to diseases and tailoring treatment accordingly.
- Precision oncology: Using genomic data to identify targeted therapies for cancer patients.
- Personalized nutrition and fitness plans: Providing tailored recommendations based on individual needs and goals.
7. The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity
As technology becomes increasingly integrated into our lives, cybersecurity is becoming paramount. Protecting sensitive data and systems from cyberattacks is crucial for individuals, businesses, and governments alike.
Implications:
- Increased Sophistication of Cyberattacks: Cybercriminals are employing increasingly sophisticated tactics to target individuals and organizations.
- Growing Need for Cybersecurity Professionals: The demand for cybersecurity professionals is increasing rapidly as organizations seek to protect their digital assets.
- Evolving Cybersecurity Regulations: Governments are implementing stricter regulations to address cybersecurity threats and protect sensitive data.
Benefits:
- Data Protection: Cybersecurity measures protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
- Business Continuity: Secure systems and data ensure business continuity and minimize disruption from cyber incidents.
- Enhanced Trust: Strong cybersecurity practices build trust with customers and partners, fostering confidence in online transactions and data sharing.
Examples:
- Multi-factor authentication: Adding layers of security to online accounts.
- Firewall and antivirus software: Protecting devices and networks from malware and cyberattacks.
- Cybersecurity awareness training: Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices and common threats.
8. The Rise of the Sharing Economy
The sharing economy, based on peer-to-peer sharing of goods and services, is rapidly expanding. This model offers greater affordability, flexibility, and sustainability, challenging traditional business models in various sectors.
Implications:
- Increased Access to Resources: The sharing economy provides access to a wider range of goods and services at lower costs, promoting affordability and accessibility.
- Reduced Ownership: Individuals are increasingly opting to access resources rather than own them, reducing consumption and promoting sustainability.
- New Business Models: The sharing economy is creating new business models and opportunities for entrepreneurs and individuals to generate income.
Benefits:
- Economic Empowerment: The sharing economy provides opportunities for individuals to earn income through sharing their assets and skills.
- Environmental Sustainability: Sharing resources reduces consumption and waste, promoting a more sustainable lifestyle.
- Community Building: The sharing economy fosters a sense of community by connecting individuals and promoting collaborative consumption.
Examples:
- Ride-sharing services: Uber, Lyft, and Ola offer convenient and affordable transportation options.
- Home-sharing platforms: Airbnb and Vrbo provide affordable lodging options for travelers.
- Skill-sharing platforms: Upwork and Fiverr connect individuals with freelance work opportunities.
FAQs about New Trends in 2025
Q: What are the most significant impacts of these trends on society?
A: These trends will profoundly impact society, leading to significant changes in how we work, live, and interact with each other. AI will automate tasks, creating new job opportunities while potentially displacing others. The metaverse will offer new avenues for social connection and immersive experiences, while sustainable technologies will address environmental concerns and promote a more sustainable future. The democratization of technology will empower individuals and communities, fostering innovation and bridging the digital divide. Personalized medicine will revolutionize healthcare, delivering targeted and effective treatments. Cybersecurity will be paramount in protecting sensitive data and systems from cyberattacks. The sharing economy will promote affordability, sustainability, and new business models.
Q: How can individuals and businesses prepare for these trends?
A: Individuals and businesses need to embrace a mindset of continuous learning and adaptation. Individuals should invest in upskilling and reskilling to acquire the skills needed in the evolving job market. Businesses should invest in emerging technologies, adopt sustainable practices, and prioritize cybersecurity. Understanding the implications of these trends and developing strategies for navigating this changing landscape is crucial for success.
Q: What are the potential risks and challenges associated with these trends?
A: While these trends offer significant opportunities, they also present challenges. The rapid adoption of AI raises concerns about job displacement and algorithmic bias. The metaverse could create new ethical dilemmas related to privacy and data security. Sustainable technologies require significant investments and may face resistance from vested interests. The democratization of technology could exacerbate existing inequalities if access is not equitable. Personalized medicine raises ethical concerns about data privacy and genetic discrimination. Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, requiring ongoing vigilance and adaptation. The sharing economy can create competition with traditional businesses and raise concerns about labor rights and worker safety.
Tips for Navigating the New Trends in 2025
- Embrace Continuous Learning: Stay updated on emerging technologies and trends, and invest in upskilling and reskilling to adapt to the changing job market.
- Foster Innovation: Encourage experimentation and explore new ways to leverage emerging technologies to solve problems and create value.
- Prioritize Sustainability: Adopt sustainable practices and invest in environmentally friendly solutions to contribute to a healthier planet.
- Embrace Collaboration: Collaborate with other individuals and organizations to share knowledge, resources, and best practices.
- Champion Digital Literacy: Promote digital literacy and empower individuals to navigate the digital world safely and responsibly.
- Promote Ethical Use of Technology: Advocate for the ethical development and use of AI and other emerging technologies to ensure equitable and responsible adoption.
Conclusion
The new trends shaping the world in 2025 present both opportunities and challenges. By understanding these trends and proactively adapting to the evolving landscape, individuals, businesses, and policymakers can navigate this dynamic future and contribute to a more prosperous and sustainable world. Embracing innovation, prioritizing sustainability, and fostering collaboration are essential for navigating this exciting and transformative era. As these trends continue to unfold, it is crucial to remain adaptable, informed, and engaged in shaping a future that benefits all.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Future: Key Trends Shaping the World in 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!