Navigating the Future: Understanding the Trends Cycle of 2025
Related Articles: Navigating the Future: Understanding the Trends Cycle of 2025
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Future: Understanding the Trends Cycle of 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Future: Understanding the Trends Cycle of 2025
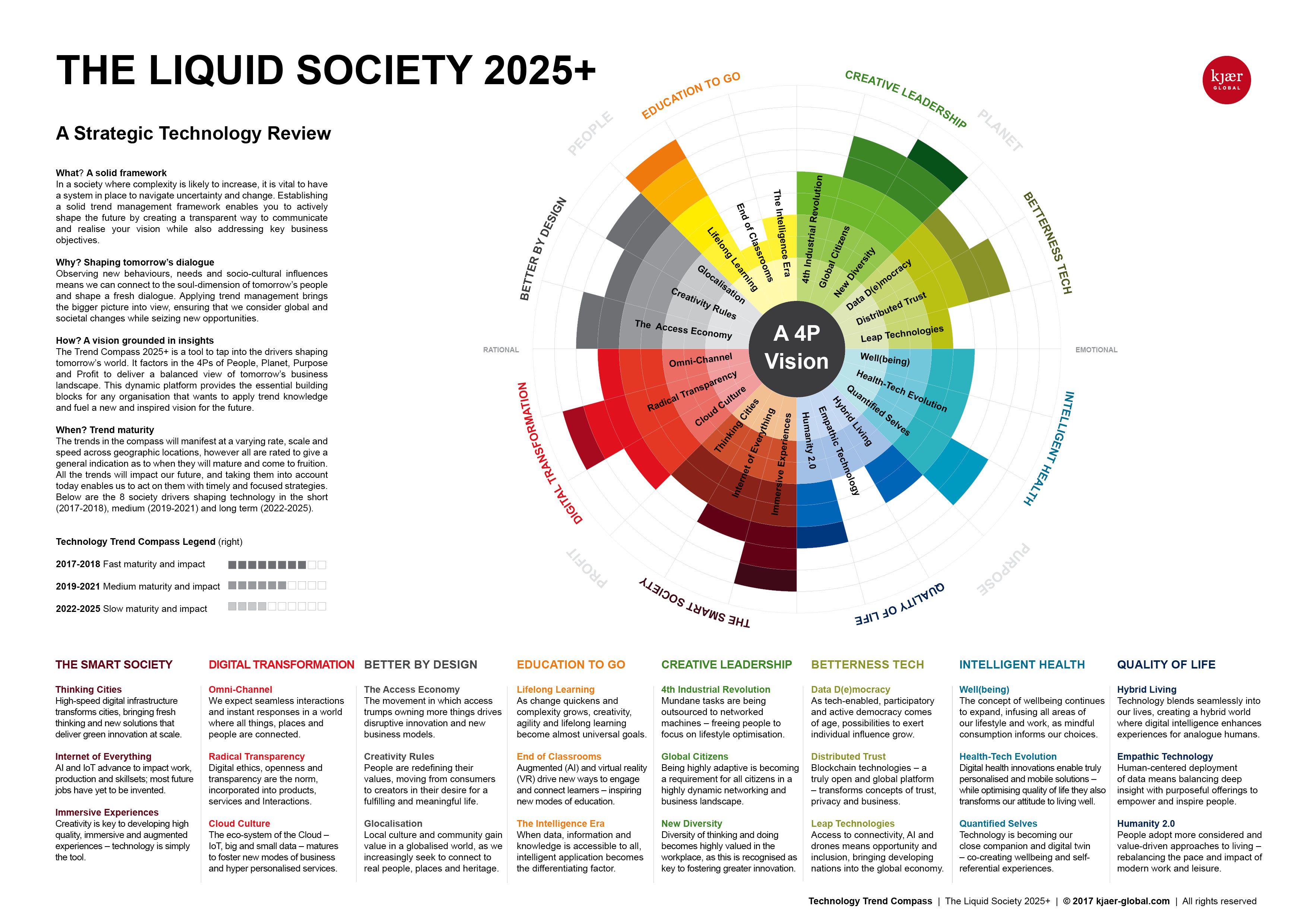
The world is in constant flux, driven by technological advancements, evolving societal values, and shifting economic landscapes. This dynamic environment necessitates a forward-looking approach, anticipating and adapting to emerging trends. Trends Cycle 2025 represents a valuable framework for understanding the key drivers shaping the future, allowing businesses, individuals, and policymakers to navigate the complexities of the coming years.
Understanding the Trends Cycle
The Trends Cycle 2025 is not a rigid prediction but rather a dynamic analysis of interconnected trends that are likely to influence various aspects of life. It encompasses a broad range of factors, from technological innovations to social and environmental concerns. By recognizing these trends, we can anticipate their potential impact and formulate proactive strategies to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks.
Key Trends Shaping the Future
1. Technological Advancements:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are rapidly transforming industries, automating tasks, enhancing decision-making, and driving innovation. From self-driving cars to personalized healthcare, these technologies are poised to revolutionize our lives.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The interconnectedness of devices, from smart homes to industrial automation, is creating a vast network of data and insights. This interconnectedness enables real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized resource management.
- Quantum Computing: This nascent technology promises to solve complex problems beyond the capabilities of classical computers, leading to breakthroughs in drug discovery, materials science, and financial modeling.
- Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering: Advancements in gene editing, personalized medicine, and synthetic biology are opening new frontiers in healthcare, agriculture, and environmental sustainability.
2. Sustainability and Climate Change:
- Renewable Energy: The transition to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and geothermal, is accelerating, driven by environmental concerns and cost reductions.
- Circular Economy: Emphasis on resource efficiency, waste reduction, and product longevity promotes sustainable practices, reducing environmental impact and fostering economic growth.
- Climate Action: Governments, businesses, and individuals are taking concrete steps to mitigate climate change, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, investing in climate-resilient infrastructure, and promoting sustainable practices.
3. Social and Demographic Shifts:
- Aging Population: Globally, populations are aging, leading to a growing demand for healthcare, retirement planning, and age-friendly infrastructure.
- Urbanization: As populations concentrate in cities, there is a need for sustainable urban planning, efficient transportation systems, and affordable housing solutions.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Promoting diversity and inclusion in all aspects of society, from workplaces to education, is crucial for fostering creativity, innovation, and social cohesion.
4. Economic Transformation:
- Globalization and Trade: International trade and interconnected economies continue to evolve, presenting opportunities for businesses to expand their reach but also posing challenges related to global competition and economic inequality.
- Gig Economy: The rise of freelance work and online platforms is changing the nature of employment, providing flexibility but also raising concerns about job security and social benefits.
- Digital Economy: The growth of online commerce, digital services, and e-commerce is transforming traditional business models and creating new opportunities for entrepreneurship.
Related Searches and In-Depth Exploration
1. Future of Work:
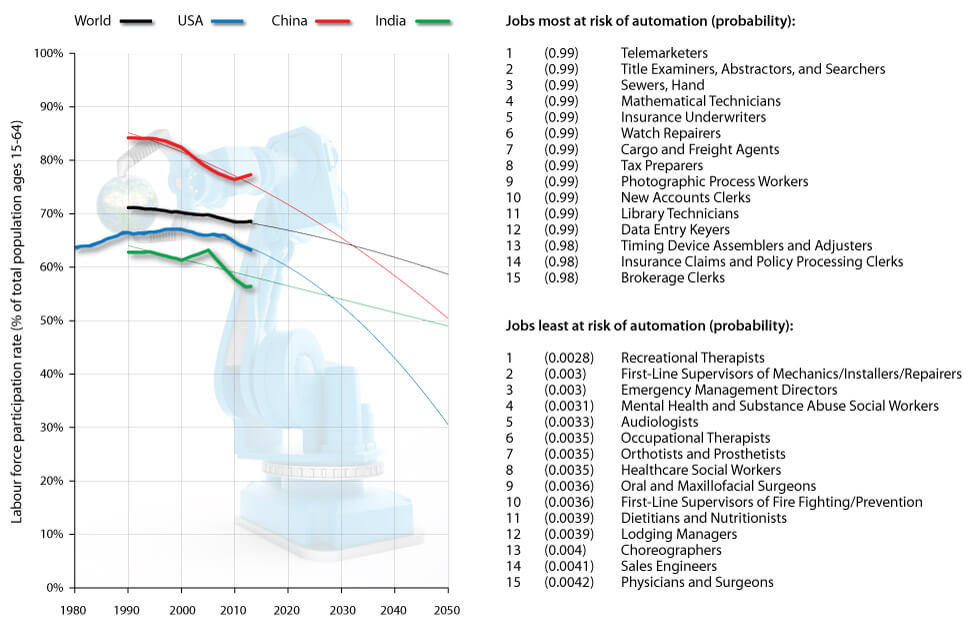
- Automation and Job Displacement: Understanding the potential impact of automation on various industries and the need for reskilling and upskilling programs to prepare the workforce for the future.
- Remote Work and Virtual Teams: The increasing prevalence of remote work and the challenges and opportunities associated with managing distributed teams, including fostering collaboration and maintaining productivity.
- Work-Life Balance and Employee Well-being: The changing nature of work and the importance of prioritizing employee well-being, including work-life balance, mental health, and flexible work arrangements.
2. Healthcare and Bioethics:
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring medical treatments to individual patients based on their genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
- Telemedicine and Remote Healthcare: The use of technology to deliver healthcare services remotely, improving accessibility and affordability.
- Ethical Considerations in Biotechnology: Debates surrounding the ethical implications of genetic engineering, gene editing, and other emerging biotechnologies.
3. Education and Skills Development:
- Lifelong Learning: The need for continuous learning and skill development throughout one’s career, as technology and job requirements evolve rapidly.
- Digital Literacy and Coding Skills: The importance of developing digital literacy and coding skills to thrive in the digital economy.
- Education for Sustainability: Integrating sustainability principles into education systems to foster environmentally responsible citizens and innovators.
4. Cybersecurity and Data Privacy:
- Data Security and Privacy: The growing importance of protecting personal data and ensuring data privacy in an increasingly digital world.
- Cyberattacks and Cybersecurity Measures: The evolving threat landscape of cyberattacks and the need for robust cybersecurity measures to protect individuals and organizations.
- Data Ethics and Artificial Intelligence: The ethical considerations surrounding the use of AI, including bias, transparency, and accountability.
5. Urban Planning and Smart Cities:
- Sustainable Urban Development: Designing cities that are environmentally sustainable, resilient to climate change, and promote social equity.
- Smart City Technologies: Utilizing technology to improve city infrastructure, transportation systems, energy efficiency, and citizen services.
- Urban Mobility and Transportation: Addressing challenges related to traffic congestion, air pollution, and promoting alternative transportation options.
6. Consumer Behavior and Marketing:
- E-commerce and Online Shopping: The growth of online shopping and the evolving consumer preferences in the digital age.
- Personalized Marketing and Customer Experience: Tailoring marketing messages and customer experiences based on individual preferences and behaviors.
- Social Media and Influencer Marketing: The impact of social media and influencer marketing on consumer decision-making and brand perception.
7. Financial Technology (FinTech):
- Digital Payments and Mobile Banking: The increasing use of digital payment methods and mobile banking applications.
- Blockchain Technology and Cryptocurrencies: The potential of blockchain technology to revolutionize financial systems and the emergence of cryptocurrencies.
- Financial Inclusion and Access to Credit: Expanding access to financial services for underserved populations through innovative technologies.
8. Governance and Policy:
- Regulation of Emerging Technologies: The need for effective regulations to govern the development and use of emerging technologies, such as AI and biotechnology.
- International Cooperation and Global Governance: Addressing global challenges, such as climate change and pandemics, through international collaboration and multilateral agreements.
- Social Responsibility and Corporate Governance: The increasing importance of businesses adopting ethical and sustainable practices and promoting social responsibility.
FAQs about Trends Cycle 2025
1. What is the purpose of understanding the Trends Cycle 2025?
Understanding the Trends Cycle 2025 enables individuals, businesses, and policymakers to anticipate future developments, make informed decisions, and prepare for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. It provides a framework for strategic planning, innovation, and adaptation in a rapidly changing world.
2. How can businesses benefit from understanding the Trends Cycle?
Businesses can leverage the Trends Cycle 2025 to identify new market opportunities, develop innovative products and services, adapt to changing consumer preferences, and stay ahead of the competition. It can also help them identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies.
3. How can individuals benefit from understanding the Trends Cycle?
Individuals can use the Trends Cycle 2025 to make informed career choices, invest in skills that will be in demand, and adapt to changing social and economic landscapes. It can also help them make more sustainable lifestyle choices and contribute to a better future.
4. What are the potential challenges of the Trends Cycle 2025?
The Trends Cycle 2025 also presents potential challenges, including job displacement due to automation, ethical concerns related to emerging technologies, and the need to address inequality and social justice issues.
5. How can we prepare for the Trends Cycle 2025?
Preparing for the Trends Cycle 2025 requires a proactive approach, including:
- Investing in education and skills development.
- Promoting innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Addressing ethical and social concerns.
- Building resilience and adaptability.
Tips for Navigating the Trends Cycle
- Stay Informed: Continuously seek out information and analysis on emerging trends to remain informed about the changing landscape.
- Develop Adaptability: Cultivate a mindset of flexibility and willingness to adapt to new technologies, skills, and opportunities.
- Embrace Innovation: Encourage creativity, experimentation, and the development of new solutions to address emerging challenges.
- Focus on Sustainability: Prioritize environmental sustainability, resource efficiency, and responsible practices in all aspects of life.
- Promote Inclusivity: Advocate for diversity, equity, and inclusion in all sectors of society.
Conclusion
The Trends Cycle 2025 serves as a roadmap for navigating the future, highlighting the transformative forces shaping our world. By understanding these trends, we can make informed decisions, seize opportunities, and mitigate risks. The future is not predetermined, but through informed action and collaboration, we can shape a brighter and more sustainable future for all.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Future: Understanding the Trends Cycle of 2025. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!