Navigating the Periodic Table: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Periodic Trends
Related Articles: Navigating the Periodic Table: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Periodic Trends
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Periodic Table: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Periodic Trends. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Periodic Table: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Periodic Trends
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Periodic Table: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Periodic Trends
- 3.1 Key Periodic Trends: A Framework for Understanding Element Behavior
- 3.2 Importance of Periodic Trends: A Foundation for Chemical Predictions
- 3.3 Exploring Related Searches: Expanding Your Knowledge
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Concerns
- 3.5 Tips for Mastering Periodic Trends: A Step-by-Step Approach
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Foundation for Deeper Chemical Understanding
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Periodic Table: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Periodic Trends
/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)
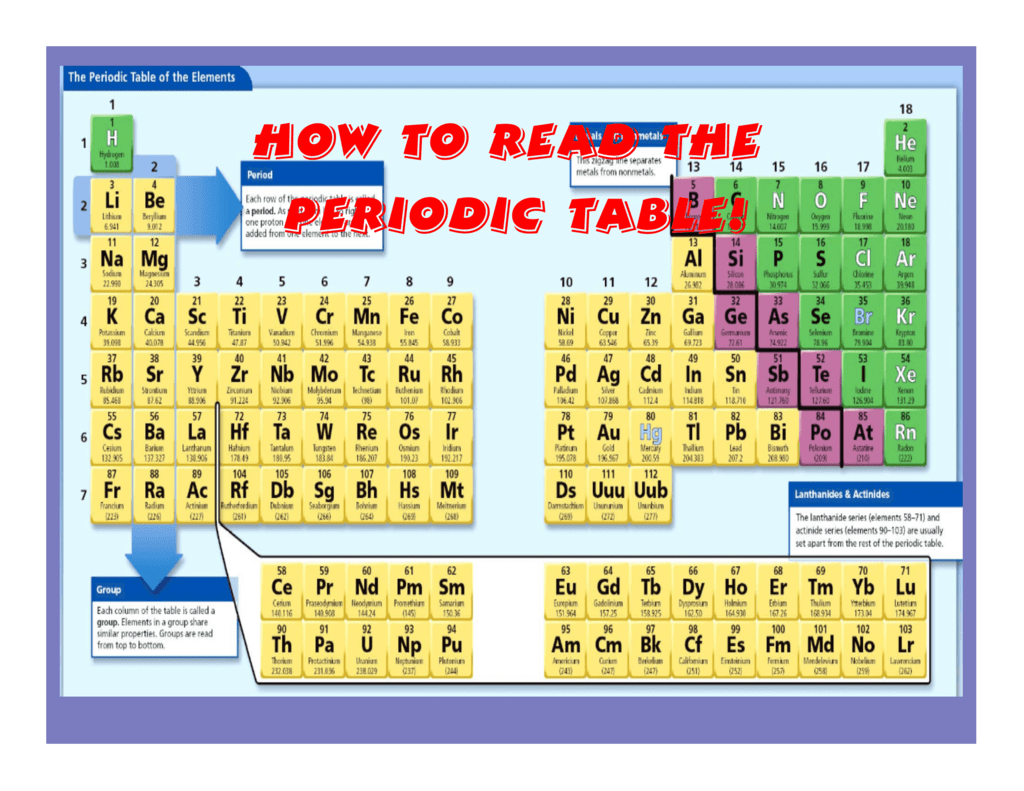
The periodic table, a fundamental tool in chemistry, organizes elements based on their atomic structure and recurring properties. Understanding the periodic trends within this table is crucial for comprehending the behavior of elements and predicting their reactions. This article delves into the key periodic trends and provides a comprehensive overview of their significance in the study of chemistry.
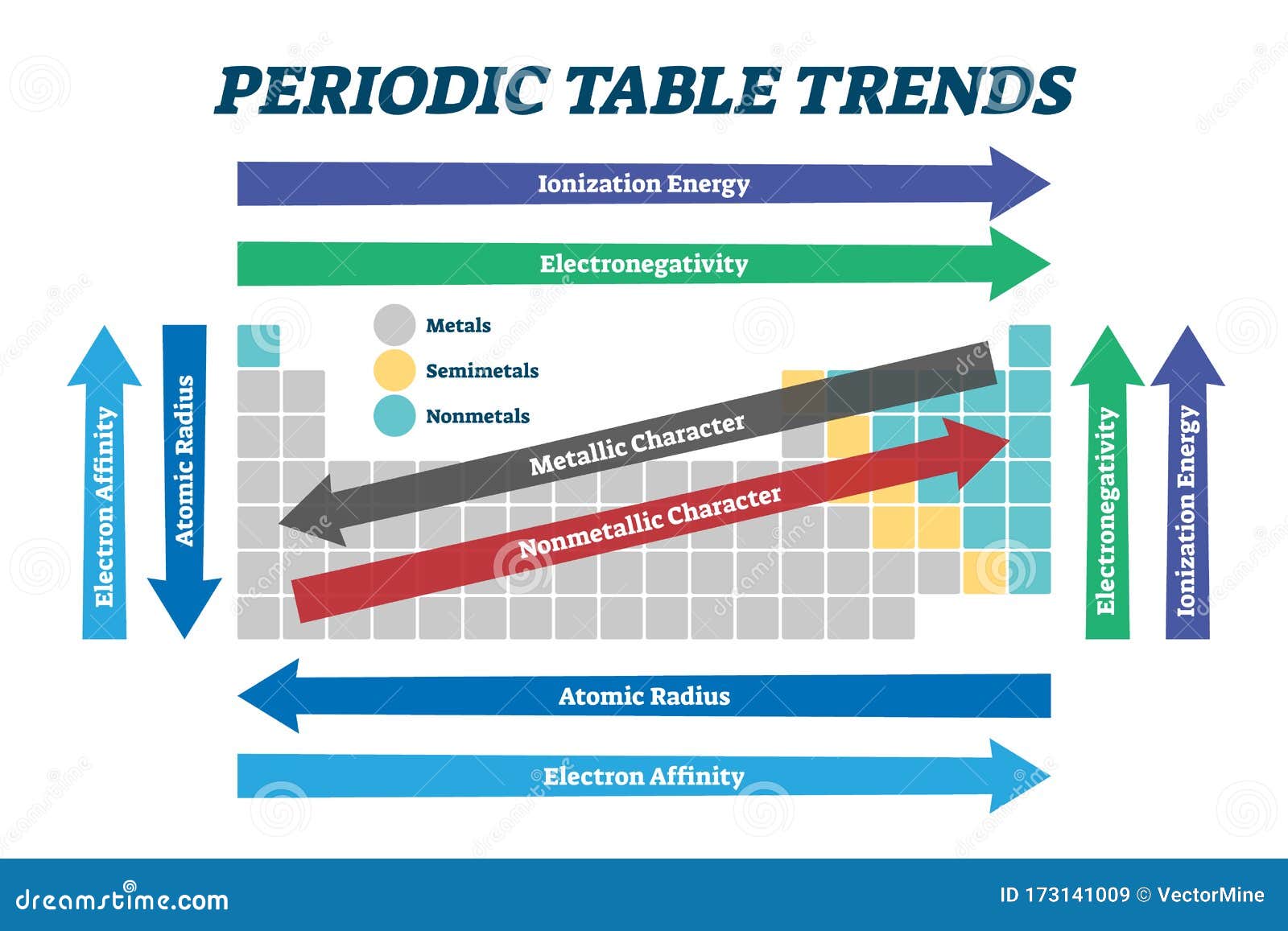
Key Periodic Trends: A Framework for Understanding Element Behavior
1. Atomic Radius:
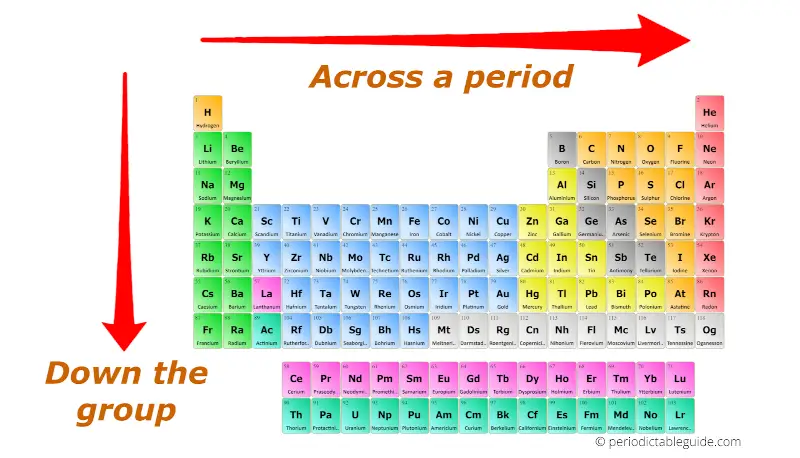
The atomic radius refers to the distance between the nucleus of an atom and its outermost electron shell. Across a period (horizontal row), the atomic radius generally decreases. This is due to increasing nuclear charge, which pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus. Moving down a group (vertical column), the atomic radius increases due to the addition of electron shells, leading to a greater distance between the nucleus and the outermost electrons.
2. Ionization Energy:
Ionization energy represents the minimum energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom in its ground state. Across a period, ionization energy generally increases due to the stronger attraction between the nucleus and electrons. Moving down a group, ionization energy decreases as the outermost electron is farther from the nucleus and experiences weaker attraction.
3. Electron Affinity:
Electron affinity is the change in energy that occurs when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom. Across a period, electron affinity generally increases as the atom becomes more stable by gaining an electron. Moving down a group, electron affinity generally decreases due to the increasing size of the atom, making it less attractive to an additional electron.
4. Electronegativity:
Electronegativity measures an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. Across a period, electronegativity increases due to the increasing nuclear charge, which pulls electrons more strongly. Moving down a group, electronegativity decreases due to the increasing distance between the nucleus and the outermost electrons.
5. Metallic Character:
Metallic character refers to the tendency of an element to lose electrons and form positive ions. Moving across a period, metallic character decreases as elements become more electronegative and less likely to lose electrons. Moving down a group, metallic character increases as the outermost electrons are farther from the nucleus and more easily removed.
Importance of Periodic Trends: A Foundation for Chemical Predictions
Understanding these periodic trends is vital for several reasons:
- Predicting Chemical Properties: Periodic trends allow us to predict the chemical behavior of elements and their compounds. For instance, elements with high electronegativity are likely to form ionic bonds, while elements with low electronegativity are more likely to form covalent bonds.
- Understanding Chemical Reactions: Periodic trends help explain the reactivity of elements and their participation in chemical reactions. For example, elements with low ionization energy tend to be reactive metals, while elements with high ionization energy are less reactive nonmetals.
- Designing New Materials: By understanding periodic trends, scientists can design new materials with specific properties. For example, knowledge of electronegativity helps in selecting elements for semiconductors and other electronic materials.
Exploring Related Searches: Expanding Your Knowledge
1. Periodic Trends Worksheet Answers PDF 2025: This search likely refers to downloadable resources that provide answers to practice problems related to periodic trends. These worksheets are invaluable for students to test their understanding of the concepts and apply them to real-world scenarios.
2. Periodic Trends Worksheet PDF: This search focuses on finding worksheets specifically designed to test understanding of periodic trends. These worksheets may cover various aspects, including atomic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity, and metallic character.
3. Periodic Trends Worksheet Answers: This search aims to find answers to periodic trends worksheets without specifying a specific year or format. This can be helpful for students looking for solutions to practice problems or for teachers seeking answers to check student work.
4. Periodic Trends Worksheet High School: This search specifically targets worksheets designed for high school chemistry students. These worksheets may include more complex problems and applications of periodic trends to real-world examples.
5. Periodic Trends Worksheet College: This search aims to find worksheets suitable for college-level chemistry courses. These worksheets may cover advanced topics and require a deeper understanding of periodic trends.
6. Periodic Trends Worksheet Answers Key: This search seeks to find answer keys for specific periodic trends worksheets. These keys can be used by students to check their work or by teachers to ensure accurate grading.
7. Periodic Trends Worksheet Printable: This search focuses on finding printable worksheets that can be used for classroom instruction or independent study. These worksheets may include a variety of question formats, including multiple choice, true/false, and short answer.
8. Periodic Trends Worksheet with Answers: This search combines the need for both worksheets and answers. This type of resource provides a convenient package for students to practice their understanding of periodic trends and check their work.
Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Concerns
1. What are the main factors that influence periodic trends?
The primary factors influencing periodic trends are:
- Nuclear Charge: The number of protons in the nucleus determines the strength of attraction between the nucleus and electrons.
- Number of Electron Shells: The number of electron shells affects the distance between the nucleus and outermost electrons.
- Shielding Effect: Inner electrons shield the outer electrons from the full attraction of the nucleus.
2. How can I remember the periodic trends?
Here are some helpful mnemonics to remember the trends:
- Atomic Radius: "Across the period, radius decreases; down the group, radius increases."
- Ionization Energy: "Across the period, ionization energy increases; down the group, ionization energy decreases."
- Electronegativity: "Across the period, electronegativity increases; down the group, electronegativity decreases."
3. Why are periodic trends important in chemistry?
Periodic trends provide a framework for understanding the behavior of elements and predicting their reactions. This knowledge is crucial for developing new materials, understanding chemical reactions, and interpreting experimental data.
4. How can I use periodic trends to predict the properties of a new element?
By understanding the trends, you can predict the properties of a new element based on its position in the periodic table. For example, if a new element is located below sodium in the periodic table, you can expect it to be more reactive than sodium and have a larger atomic radius.
5. Are there any exceptions to periodic trends?
Yes, there are some exceptions to periodic trends. For example, the ionization energy of nitrogen is higher than oxygen, even though oxygen has a higher nuclear charge. This is due to the half-filled electron configuration of nitrogen, which makes it more stable and requires more energy to remove an electron.
Tips for Mastering Periodic Trends: A Step-by-Step Approach
1. Visualize the Periodic Table: Familiarize yourself with the layout of the periodic table, including the location of groups and periods.
2. Understand the Underlying Principles: Focus on the factors that influence periodic trends, such as nuclear charge, number of electron shells, and shielding effect.
3. Use Mnemonics: Employ mnemonics to remember the general trends for atomic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity, and metallic character.
4. Practice with Worksheets: Work through periodic trends worksheets to apply your knowledge and test your understanding.
5. Connect Trends to Real-World Examples: Relate periodic trends to real-world applications, such as the reactivity of metals, the properties of semiconductors, and the formation of ionic and covalent bonds.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Deeper Chemical Understanding
Understanding periodic trends is essential for mastering chemistry. These trends provide a framework for predicting the behavior of elements and their compounds, understanding chemical reactions, and designing new materials. By studying the periodic table and its trends, you gain a deeper understanding of the fundamental principles that govern the world around us.

.PNG)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Periodic Table: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Periodic Trends. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!