Shaping the Future: Industrial Trends for 2025 and Beyond
Related Articles: Shaping the Future: Industrial Trends for 2025 and Beyond
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Shaping the Future: Industrial Trends for 2025 and Beyond. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shaping the Future: Industrial Trends for 2025 and Beyond

The industrial landscape is in constant flux, driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer demands, and global economic shifts. As we stand on the precipice of 2025, understanding the key industrial trends shaping the future is not just an option, but a necessity for businesses seeking to thrive.
This exploration delves into eight pivotal trends impacting the industrial world in 2025 and beyond, highlighting their potential impact and offering insights into how businesses can leverage them for success.
1. The Rise of Industry 4.0: Automation and Digital Transformation
Industry 4.0, the fourth industrial revolution, is characterized by the convergence of physical and digital technologies. This trend is fundamentally altering how industries operate, with automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics becoming integral components of production, logistics, and decision-making.
- Automation: Robots and cobots (collaborative robots) are increasingly replacing manual labor in repetitive or hazardous tasks, leading to enhanced productivity, reduced errors, and improved safety.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms are transforming industries by analyzing vast datasets to optimize processes, predict demand, personalize customer experiences, and even develop new products and services.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The interconnectedness of devices through the IoT enables real-time data collection and analysis, facilitating predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and optimized resource allocation.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms offer scalable and cost-effective solutions for data storage, processing, and application deployment, enabling businesses to access advanced technologies without significant upfront investments.
Benefits of Industry 4.0:
- Increased Productivity: Automation and AI streamline processes, reducing waste and boosting output.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Data-driven insights optimize operations, leading to more efficient resource utilization.
- Improved Quality: Automation and AI minimize human error, resulting in higher product quality and consistency.
- Cost Reduction: Automation and process optimization contribute to lower production costs and increased profitability.
- Enhanced Safety: Automation removes humans from hazardous environments, improving workplace safety.
2. Sustainability: A Core Value in Industrial Operations
Environmental concerns are no longer a peripheral consideration; they are central to business operations. Companies are increasingly prioritizing sustainable practices across their value chains, driven by both regulatory pressure and consumer demand.
- Renewable Energy: Businesses are embracing renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro to reduce their carbon footprint and mitigate dependence on fossil fuels.
- Circular Economy: The circular economy model emphasizes reducing waste, reusing materials, and recycling resources, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing resource efficiency.
- Sustainable Materials: Companies are exploring and implementing sustainable materials like recycled plastics, bio-based polymers, and sustainable forestry products to minimize their environmental footprint.
- Energy Efficiency: Investing in energy-efficient technologies and processes helps reduce energy consumption, lower costs, and contribute to environmental sustainability.
Benefits of Sustainability:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Sustainable practices minimize pollution, conserve resources, and mitigate climate change.
- Cost Savings: Energy efficiency, waste reduction, and resource optimization lead to lower operational costs.
- Enhanced Brand Reputation: Companies committed to sustainability attract environmentally conscious consumers and investors.
- Improved Compliance: Meeting regulatory requirements and adhering to sustainability standards fosters trust and minimizes legal risks.
3. The Rise of Personalized Products and Services
Consumers are increasingly demanding personalized experiences, and industries are responding by tailoring products and services to individual needs and preferences. This trend is driven by the proliferation of data and the ability to analyze customer behavior and preferences.
- Mass Customization: Manufacturing processes are becoming more flexible, enabling companies to produce customized products on a large scale, meeting specific customer requirements.
- Data-Driven Personalization: Companies leverage customer data to personalize marketing campaigns, product recommendations, and service offerings, creating a more engaging and relevant customer experience.
- Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Models: Businesses are increasingly bypassing traditional retail channels and selling directly to consumers, allowing for greater control over the customer journey and personalized interactions.
- Subscription Models: Subscription services offer a flexible and personalized way for consumers to access products and services, providing ongoing value and recurring revenue streams for businesses.
Benefits of Personalized Products and Services:
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Personalized experiences enhance customer engagement and loyalty.
- Higher Revenue Generation: Tailored products and services cater to specific needs, leading to increased sales and profitability.
- Enhanced Brand Loyalty: Personalized interactions build stronger customer relationships and foster brand advocacy.
- Improved Market Competitiveness: Offering unique and personalized experiences differentiates businesses in a crowded marketplace.
4. The Importance of Cybersecurity in a Connected World
As industries become increasingly reliant on digital technologies, cybersecurity becomes paramount. Protecting sensitive data, critical infrastructure, and intellectual property from cyberattacks is essential for maintaining business continuity and safeguarding reputation.
- Data Security and Privacy: Companies must implement robust data security measures to protect sensitive customer information, financial data, and intellectual property from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Network Security: Secure network infrastructure is crucial to prevent cyberattacks and unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Cybersecurity Training: Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices and threats helps prevent human error and reduces the risk of cyberattacks.
- Incident Response Plans: Having a well-defined incident response plan in place allows businesses to quickly and effectively respond to cyberattacks, minimizing damage and ensuring business continuity.
Benefits of Robust Cybersecurity:
- Data Protection: Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches safeguards customer trust and business operations.
- Business Continuity: Strong cybersecurity measures ensure uninterrupted business operations in the event of a cyberattack.
- Financial Security: Protecting financial data prevents fraud and financial losses.
- Enhanced Reputation: A strong cybersecurity posture builds trust and confidence among stakeholders.
5. The Growth of E-commerce and Digital Sales Channels
The rise of e-commerce and digital sales channels is transforming how businesses connect with customers. Online marketplaces, mobile apps, and social media platforms are providing new avenues for businesses to reach wider audiences and sell products and services.
- Online Marketplaces: Platforms like Amazon, eBay, and Alibaba provide businesses with access to a vast global customer base, expanding their reach and increasing sales opportunities.
- Mobile Commerce: Mobile apps and responsive websites allow businesses to engage customers on the go, providing a seamless shopping experience across devices.
- Social Media Commerce: Social media platforms are becoming increasingly important for driving sales, allowing businesses to connect with customers, showcase products, and facilitate direct purchases.
- Digital Marketing and Advertising: Businesses are leveraging digital marketing strategies like search engine optimization (SEO), pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, and social media marketing to reach their target audience and drive online sales.
Benefits of E-commerce and Digital Sales Channels:
- Expanded Reach: Online platforms connect businesses with a global audience, increasing their potential customer base.
- Increased Sales: E-commerce provides a convenient and accessible platform for customers, driving increased sales and revenue.
- Reduced Costs: Digital sales channels often involve lower overhead costs compared to traditional retail operations.
- Data-Driven Insights: E-commerce platforms provide valuable data about customer behavior, allowing businesses to optimize their strategies and improve customer experiences.
6. The Workforce of the Future: Skills and Talent Development
The changing industrial landscape requires a workforce equipped with the skills and knowledge to thrive in a technology-driven environment. Businesses are investing in training and development programs to upskill their workforce and attract top talent.
- Technical Skills: Demand for workers with technical skills in areas like data science, AI, robotics, and cybersecurity is increasing rapidly.
- Soft Skills: Soft skills like critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and collaboration are becoming increasingly important for success in a collaborative and technologically advanced workplace.
- Lifelong Learning: Continuous learning and upskilling are essential for employees to stay competitive and adapt to the evolving demands of the workplace.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Creating a diverse and inclusive workforce fosters innovation, creativity, and a broader range of perspectives, leading to better decision-making and problem-solving.
Benefits of a Skilled and Adaptable Workforce:
- Increased Productivity: A skilled workforce operates more efficiently, leading to higher productivity and output.
- Innovation and Creativity: Diverse perspectives and expertise drive innovation and creative problem-solving.
- Improved Customer Service: A knowledgeable and skilled workforce provides better customer service, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses with a skilled and adaptable workforce are better equipped to compete in a rapidly evolving market.
7. The Importance of Supply Chain Resilience and Agility
Supply chain disruptions, geopolitical tensions, and global economic fluctuations highlight the importance of building resilient and agile supply chains. Businesses are implementing strategies to mitigate risks and adapt to changing market conditions.
- Supply Chain Diversification: Businesses are diversifying their supplier base and geographic locations to reduce dependence on any single supplier or region.
- Inventory Management Optimization: Advanced inventory management systems and data analytics help businesses optimize inventory levels, reduce waste, and minimize disruptions.
- Real-time Visibility: Real-time tracking and monitoring of goods throughout the supply chain provide greater visibility and enable faster response to disruptions.
- Agile Manufacturing: Adopting flexible manufacturing processes and technologies allows businesses to quickly adapt production to meet changing demand and address disruptions.
Benefits of Supply Chain Resilience and Agility:
- Reduced Risk: A resilient supply chain mitigates disruptions, minimizing financial losses and reputational damage.
- Enhanced Responsiveness: Agile supply chains allow businesses to quickly adapt to changing market conditions and customer demands.
- Improved Efficiency: Optimized inventory management and real-time visibility lead to increased efficiency and reduced costs.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses with resilient and agile supply chains are better positioned to navigate market volatility and gain a competitive edge.
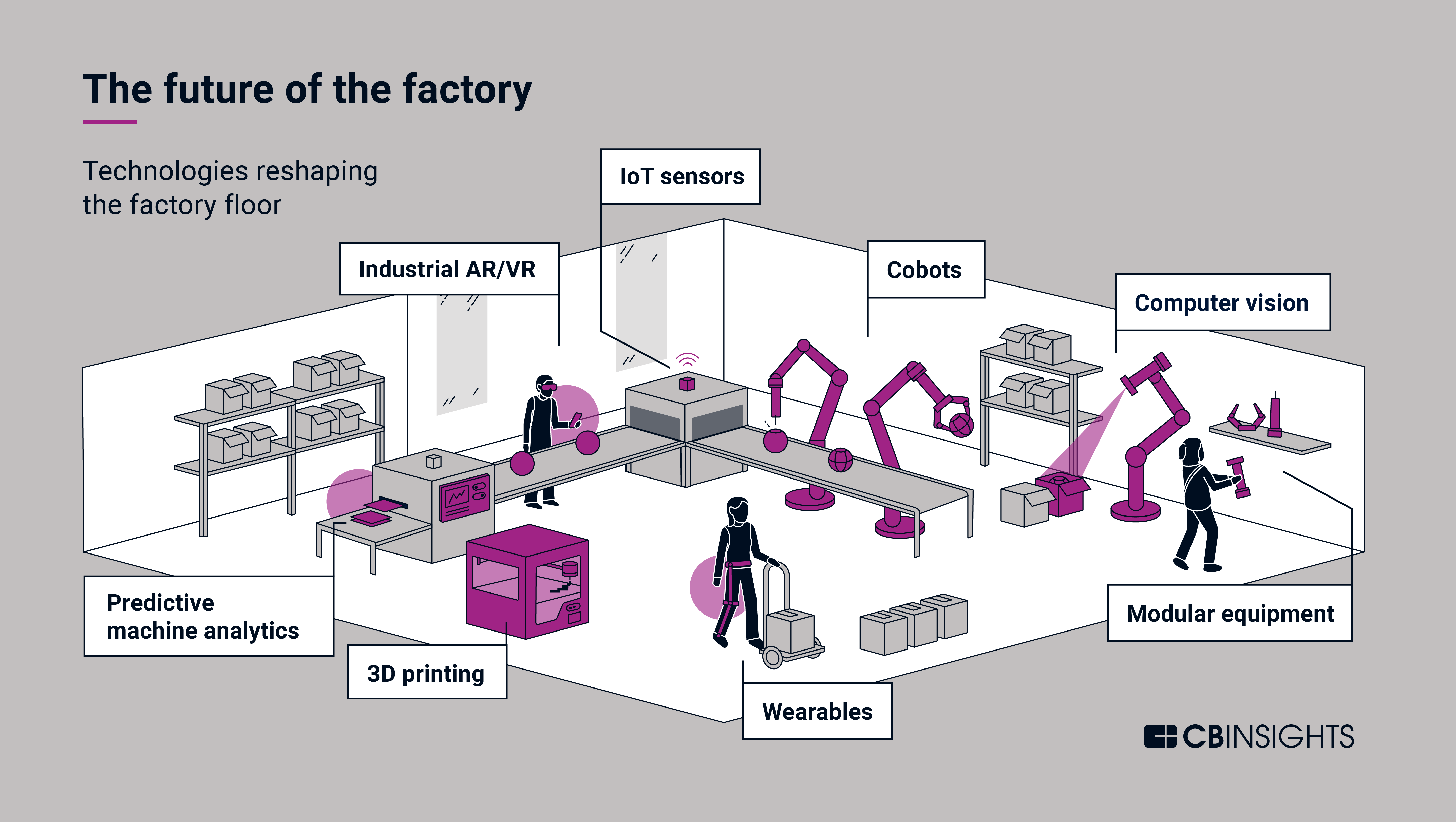
8. The Rise of Smart Factories and Advanced Manufacturing
Smart factories are transforming the manufacturing landscape by leveraging advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and robotics to optimize production processes, improve efficiency, and enhance quality.
- Automated Production Lines: Robots and cobots are automating tasks on production lines, increasing efficiency, reducing errors, and improving safety.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI-powered systems analyze data from sensors and equipment to predict maintenance needs, preventing downtime and optimizing equipment lifespan.
- Data-Driven Optimization: Real-time data collection and analysis enable manufacturers to optimize production schedules, resource allocation, and product quality.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): 3D printing allows for on-demand production of customized parts and products, reducing lead times and enabling greater flexibility.
Benefits of Smart Factories and Advanced Manufacturing:
- Increased Productivity: Automation and optimization lead to higher production rates and reduced downtime.
- Enhanced Quality: Data-driven insights and automation contribute to improved product quality and consistency.
- Reduced Costs: Optimized processes, reduced waste, and predictive maintenance contribute to lower production costs.
- Greater Flexibility: Smart factories can adapt to changing demand and produce customized products, enhancing flexibility and responsiveness.
Related Searches
- Industrial Automation Trends 2025: This search focuses on the specific advancements in automation technologies impacting industrial operations.
- Digital Transformation in Industry 2025: This search explores the broader impact of digital technologies on industrial processes, workflows, and business models.
- Future of Manufacturing 2025: This search examines the long-term implications of emerging technologies and trends on the manufacturing industry.
- Sustainable Manufacturing Trends 2025: This search delves into the specific trends and innovations driving sustainable practices in manufacturing.
- Industrial Robotics Trends 2025: This search focuses on the latest developments and applications of robotics in industrial settings.
- Artificial Intelligence in Industry 2025: This search explores the role of AI in optimizing industrial processes, decision-making, and product development.
- Internet of Things in Industry 2025: This search examines the impact of IoT connectivity on data collection, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance in industrial environments.
- Industrial Cybersecurity Trends 2025: This search focuses on the evolving threats and solutions in protecting industrial systems and data from cyberattacks.
FAQs
Q: What are the biggest challenges facing industrial businesses in 2025?
A: Industrial businesses face challenges related to technological adoption, workforce skills gaps, cybersecurity threats, supply chain disruptions, and environmental sustainability.
Q: How can businesses prepare for the industrial trends of 2025?
A: Businesses need to invest in digital transformation, embrace sustainable practices, prioritize cybersecurity, develop a skilled workforce, and build resilient supply chains.
Q: What are the potential benefits of adopting these industrial trends?
A: Adopting these trends can lead to increased productivity, improved efficiency, enhanced quality, cost reduction, greater flexibility, and improved sustainability.
Q: How can small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) benefit from these trends?
A: SMEs can leverage cloud computing platforms, affordable automation solutions, and digital marketing strategies to compete with larger businesses.
Tips
- Embrace Continuous Learning: Stay updated on emerging technologies and trends through industry publications, conferences, and online courses.
- Invest in Workforce Development: Train employees on new technologies, soft skills, and sustainability practices.
- Foster Innovation: Encourage experimentation and collaboration to develop new solutions and improve processes.
- Build Strong Partnerships: Collaborate with technology providers, research institutions, and other stakeholders to leverage expertise and drive innovation.
- Focus on Customer Experience: Use data and technology to understand customer needs and personalize products and services.
Conclusion
The industrial trends shaping the future offer both challenges and opportunities. Businesses that embrace these trends, adapt to the changing landscape, and invest in innovation, technology, and workforce development will be well-positioned to thrive in the years to come. By embracing these trends, businesses can unlock new possibilities, optimize operations, enhance competitiveness, and contribute to a more sustainable and prosperous future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shaping the Future: Industrial Trends for 2025 and Beyond. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!