Shaping the Future of Food: Trends in Food Science and Technology by 2025
Related Articles: Shaping the Future of Food: Trends in Food Science and Technology by 2025
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Shaping the Future of Food: Trends in Food Science and Technology by 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Shaping the Future of Food: Trends in Food Science and Technology by 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Shaping the Future of Food: Trends in Food Science and Technology by 2025
- 3.1 1. Personalized Nutrition and Precision Agriculture
- 3.2 2. Plant-Based Alternatives and Cellular Agriculture
- 3.3 3. Food Waste Reduction and Upcycling
- 3.4 4. Food Safety and Traceability
- 3.5 5. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Food Science
- 3.6 6. Novel Food Ingredients and Processing Technologies
- 3.7 7. Food Packaging Innovations
- 3.8 8. Consumer Education and Empowerment
- 4 Exploring Related Searches
- 4.9 Related Searches
- 5 FAQs by Trends of Food Science and Technology 2025
- 6 Tips by Trends of Food Science and Technology 2025
- 7 Conclusion by Trends of Food Science and Technology 2025
- 8 Closure
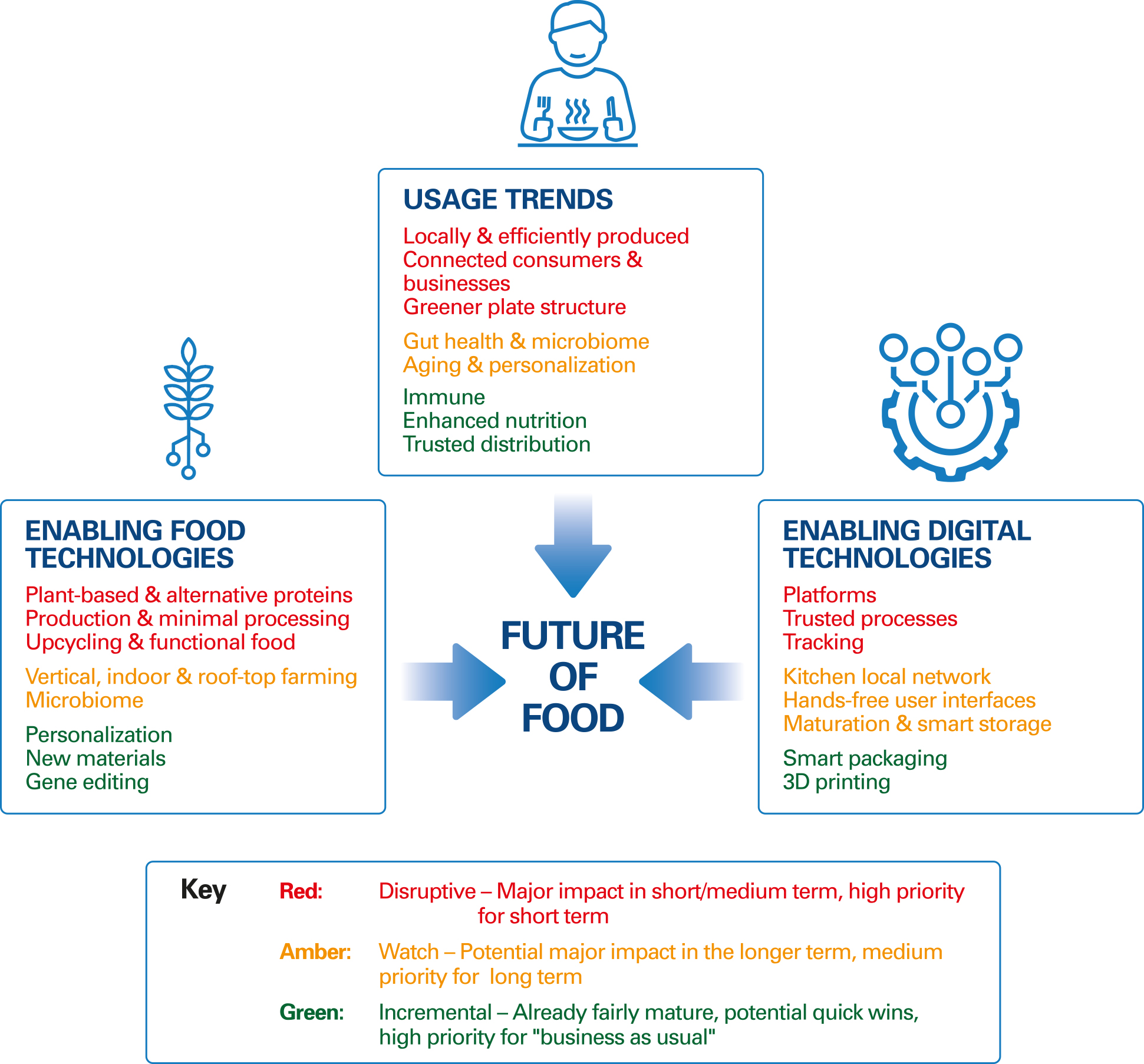
Shaping the Future of Food: Trends in Food Science and Technology by 2025

The world’s population is projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, placing immense pressure on food production and distribution systems. To meet this growing demand while ensuring food security and sustainability, food science and technology are rapidly evolving. This article delves into key trends shaping the future of food by 2025, examining their impact on production, consumption, and the overall food system.
1. Personalized Nutrition and Precision Agriculture
Personalized nutrition aims to tailor dietary recommendations to individual needs based on factors like genetics, microbiome, and lifestyle. This approach utilizes advanced technologies like genomics, metabolomics, and artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze individual data and provide customized dietary guidance.
Precision agriculture, on the other hand, focuses on optimizing crop production through data-driven insights. Sensors, drones, and satellite imagery are employed to monitor soil conditions, identify pest infestations, and optimize irrigation and fertilization strategies. This data-driven approach enables efficient resource allocation and reduces environmental impact.
Benefits:
- Improved health outcomes: Personalized nutrition can help prevent chronic diseases and optimize individual well-being.
- Enhanced food security: Precision agriculture increases crop yields and reduces food waste.
- Sustainable food production: Optimized resource management minimizes environmental footprint.
Example: Companies are developing personalized nutrition apps that analyze dietary preferences, health goals, and genetic data to provide customized meal plans and supplement recommendations. In agriculture, sensors are being used to monitor soil moisture levels, enabling farmers to optimize irrigation and conserve water.
2. Plant-Based Alternatives and Cellular Agriculture
Plant-based alternatives are gaining popularity as consumers seek healthier, more sustainable food options. These alternatives mimic the taste, texture, and nutritional content of animal-based products using ingredients like legumes, grains, and vegetables.
Cellular agriculture, also known as "cultured meat," involves growing animal cells in a laboratory setting to produce meat without raising livestock. This technology has the potential to revolutionize meat production, reducing environmental impact and animal welfare concerns.
Benefits:
- Reduced environmental footprint: Plant-based alternatives and cellular agriculture minimize land use, water consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Enhanced animal welfare: Cellular agriculture eliminates the need to raise animals for food.
- Healthier food options: Plant-based alternatives often provide a lower-fat, higher-fiber alternative to traditional meat products.
Example: Plant-based meat alternatives like Impossible Burger and Beyond Meat are becoming increasingly popular. Several companies are developing and scaling up cellular agriculture technologies to produce cultured meat products.
3. Food Waste Reduction and Upcycling
Food waste is a significant global problem, contributing to environmental degradation and food insecurity. Innovative technologies and strategies are being developed to reduce food waste at every stage of the supply chain.
Food upcycling involves transforming food waste into valuable products. This can include using food scraps to create compost, animal feed, or even new food products.
Benefits:
- Reduced environmental impact: Food waste decomposition releases greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change. Reducing waste minimizes this impact.
- Enhanced resource utilization: Upcycling food waste reduces reliance on virgin resources and promotes a circular economy.
- Improved food security: Food waste reduction ensures that more food reaches consumers, combating hunger and malnutrition.
Example: Companies are developing smart packaging that monitors food freshness and extends shelf life. Food waste is being used to produce bioplastics, animal feed, and even edible ingredients for new food products.
4. Food Safety and Traceability
Food safety remains a paramount concern, with outbreaks of foodborne illnesses posing a significant threat to public health. Advanced technologies are being implemented to enhance food safety measures and ensure the traceability of food products.
Food traceability involves tracking the origin, processing, and distribution of food products throughout the supply chain. This information is crucial for identifying the source of contamination in case of an outbreak and for ensuring the authenticity of products.
Benefits:
- Improved public health: Enhanced food safety measures reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses.
- Increased consumer confidence: Traceability provides consumers with transparency and assurance about the origin and quality of their food.
- Efficient recall processes: In case of a product recall, traceability enables swift and accurate identification of affected products.
Example: Blockchain technology is being used to create secure and transparent food traceability systems. Sensors are being integrated into packaging to monitor temperature and other critical factors throughout the supply chain.
5. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Food Science
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming food science by providing insights and automation capabilities. These technologies can analyze vast datasets to identify trends, predict consumer preferences, optimize production processes, and develop new food products.
Benefits:
- Improved product development: AI can analyze consumer data to identify emerging trends and develop new products that meet evolving tastes.
- Optimized production processes: AI-powered systems can predict and prevent production issues, enhancing efficiency and reducing waste.
- Enhanced food safety: AI can analyze real-time data to detect potential food safety hazards and alert authorities.
Example: AI-powered systems are being used to analyze consumer reviews and social media data to identify food trends. Machine learning algorithms are being employed to predict crop yields and optimize fertilizer application.
6. Novel Food Ingredients and Processing Technologies
Novel food ingredients are emerging as alternatives to traditional ingredients. These include ingredients derived from insects, algae, and other unconventional sources.
Advanced processing technologies are being developed to enhance food quality, extend shelf life, and create new product formats. These technologies include high-pressure processing (HPP), pulsed electric fields (PEF), and ultrasound processing.
Benefits:
- Increased food diversity: Novel ingredients provide new flavors, textures, and nutritional profiles.
- Sustainable food production: Some novel ingredients offer a more sustainable alternative to traditional ingredients.
- Improved food safety and quality: Advanced processing technologies can enhance food safety and extend shelf life.
Example: Insect-based protein powders are gaining popularity as a sustainable and nutritious source of protein. High-pressure processing is being used to preserve the freshness and quality of fresh produce.
7. Food Packaging Innovations
Food packaging plays a crucial role in preserving food quality, extending shelf life, and minimizing waste. Innovative packaging solutions are being developed to enhance functionality and sustainability.
Benefits:
- Improved food preservation: Innovative packaging materials can protect food from damage, contamination, and spoilage.
- Reduced food waste: Packaging solutions that extend shelf life and minimize spoilage contribute to reducing food waste.
- Sustainable packaging: Biodegradable and compostable packaging materials are being developed to reduce environmental impact.
Example: Active packaging materials are being developed that absorb moisture or release gases to extend shelf life. Biodegradable and compostable packaging options are becoming increasingly available.
8. Consumer Education and Empowerment
Consumer education is crucial for promoting healthy eating habits and informed food choices. Educational initiatives and resources are being developed to empower consumers with knowledge about food production, nutrition, and sustainability.
Benefits:
- Improved dietary choices: Informed consumers can make healthier and more sustainable food choices.
- Increased demand for sustainable food: Consumer awareness can drive demand for sustainable food products.
- Enhanced food system transparency: Educated consumers can hold food producers and retailers accountable for ethical and sustainable practices.
Example: Educational campaigns are being launched to raise awareness about the benefits of plant-based diets and sustainable food production. Online resources and apps are providing consumers with information on food nutrition and safety.
Exploring Related Searches
Related Searches
- Future of Food Trends: This search explores broader trends shaping the future of food, encompassing topics like urbanization, climate change, and consumer preferences.
- Food Technology Innovations: This search focuses on specific technological advancements in food science, including areas like genetic engineering, 3D food printing, and nanotechnology.
- Sustainable Food Systems: This search examines approaches to building more sustainable food systems, considering aspects like resource efficiency, environmental impact, and social equity.
- Food Security and Nutrition: This search delves into the challenges of global food security and explores strategies to ensure access to nutritious food for all.
- Food Waste Solutions: This search explores various approaches to reducing food waste, including technologies, policies, and consumer behavior changes.
- Plant-Based Meat Alternatives: This search focuses specifically on the development and market trends of plant-based alternatives to meat products.
- Cellular Agriculture Market: This search examines the emerging market for cultured meat and other cellular agriculture products.
- Food Packaging Trends: This search explores innovations in food packaging, including materials, technologies, and sustainability considerations.
FAQs by Trends of Food Science and Technology 2025
Q: What are the key drivers of these trends in food science and technology?
A: The drivers of these trends include:
- Growing global population: The increasing demand for food necessitates innovative solutions to ensure food security.
- Climate change: The need to mitigate the environmental impact of food production is driving the adoption of sustainable practices.
- Changing consumer preferences: Consumers are increasingly demanding healthier, more sustainable, and ethically produced food.
- Technological advancements: Innovations in areas like AI, biotechnology, and robotics are enabling new approaches to food production and consumption.
Q: How will these trends impact the food industry?
A: These trends will significantly reshape the food industry, leading to:
- New business models: Companies will need to adapt to changing consumer demands and adopt innovative technologies.
- Increased competition: New players are entering the food market, offering innovative products and services.
- Shifting consumer behavior: Consumers are becoming more discerning about their food choices, prioritizing sustainability and health.
Q: What are the potential challenges associated with these trends?
A: Challenges include:
- Cost and accessibility: New technologies and products may be initially expensive, limiting access for some consumers.
- Regulatory hurdles: New food technologies and ingredients may require new regulations and approvals.
- Public acceptance: Consumers may have concerns about the safety and ethical implications of new technologies.
Q: What role can consumers play in shaping the future of food?
A: Consumers can play a vital role by:
- Making informed choices: Choosing sustainable and healthy food options.
- Supporting innovative companies: Patronizing companies that are developing sustainable and ethical food solutions.
- Advocating for change: Encouraging policymakers to implement policies that promote food security and sustainability.
Tips by Trends of Food Science and Technology 2025
- Stay informed: Follow industry trends and research advancements in food science and technology.
- Embrace innovation: Be open to trying new food products and technologies.
- Support sustainable practices: Choose food products that are produced sustainably and minimize food waste.
- Advocate for change: Support initiatives that promote food security, sustainability, and ethical food production.
Conclusion by Trends of Food Science and Technology 2025
Food science and technology are at the forefront of addressing the challenges of feeding a growing population while ensuring food security and sustainability. By embracing these trends, we can create a more resilient, equitable, and healthy food system for the future. The innovations and advancements in food science and technology offer a promising path towards a future where everyone has access to nutritious and sustainable food.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shaping the Future of Food: Trends in Food Science and Technology by 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!