Shaping the Future: Trends in Manufacturing Industry 2025
Related Articles: Shaping the Future: Trends in Manufacturing Industry 2025
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Shaping the Future: Trends in Manufacturing Industry 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shaping the Future: Trends in Manufacturing Industry 2025

The manufacturing industry is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer demands, and the need for greater sustainability. As we approach 2025, several key trends are poised to reshape the industry landscape, ushering in a new era of efficiency, innovation, and resilience.
1. Digital Transformation:
- The Rise of Industry 4.0: The integration of digital technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing is driving the fourth industrial revolution. This revolution, known as Industry 4.0, is fundamentally changing how products are designed, manufactured, and delivered.
- Smart Factories: Connected factories leverage data analytics, machine learning, and predictive maintenance to optimize production processes, reduce downtime, and improve product quality. These factories are becoming increasingly autonomous, with robots and automated systems taking on more complex tasks.
- Digital Twins: Virtual representations of physical assets, known as digital twins, are enabling manufacturers to simulate and optimize production processes before implementation. This allows for faster prototyping, reduced errors, and improved product performance.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Real-time data collection and analysis are empowering manufacturers to make data-driven decisions, improving resource allocation, forecasting demand, and identifying potential bottlenecks.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Digital transformation optimizes production processes, minimizes waste, and increases productivity.
- Improved Quality: Data-driven insights and automated systems lead to higher product quality and consistency.
- Increased Flexibility: Smart factories are more adaptable to changing demands and can easily adjust production lines.
- Reduced Costs: Automation and optimization reduce labor costs, material waste, and downtime.
2. Sustainable Manufacturing:
- Circular Economy: Manufacturers are embracing circular economy principles, aiming to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization. This involves designing products for reuse, recycling, and remanufacturing.
- Renewable Energy: Increasingly, manufacturers are adopting renewable energy sources like solar and wind power to reduce their environmental footprint and achieve sustainability goals.
- Sustainable Materials: The use of sustainable materials like recycled plastics, bio-based materials, and sustainable wood is gaining traction, minimizing reliance on virgin resources.
- Eco-Friendly Packaging: Manufacturers are shifting towards sustainable packaging solutions, reducing the use of plastic and promoting biodegradable materials.
Benefits:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Sustainable manufacturing practices minimize pollution, conserve resources, and combat climate change.
- Cost Savings: Efficient resource utilization and waste reduction can lead to significant cost savings.
- Enhanced Brand Reputation: Consumers are increasingly demanding sustainable products, making it essential for manufacturers to adopt ethical practices.
- Compliance with Regulations: Governments are introducing stricter regulations regarding environmental impact, making sustainability a necessity for businesses.
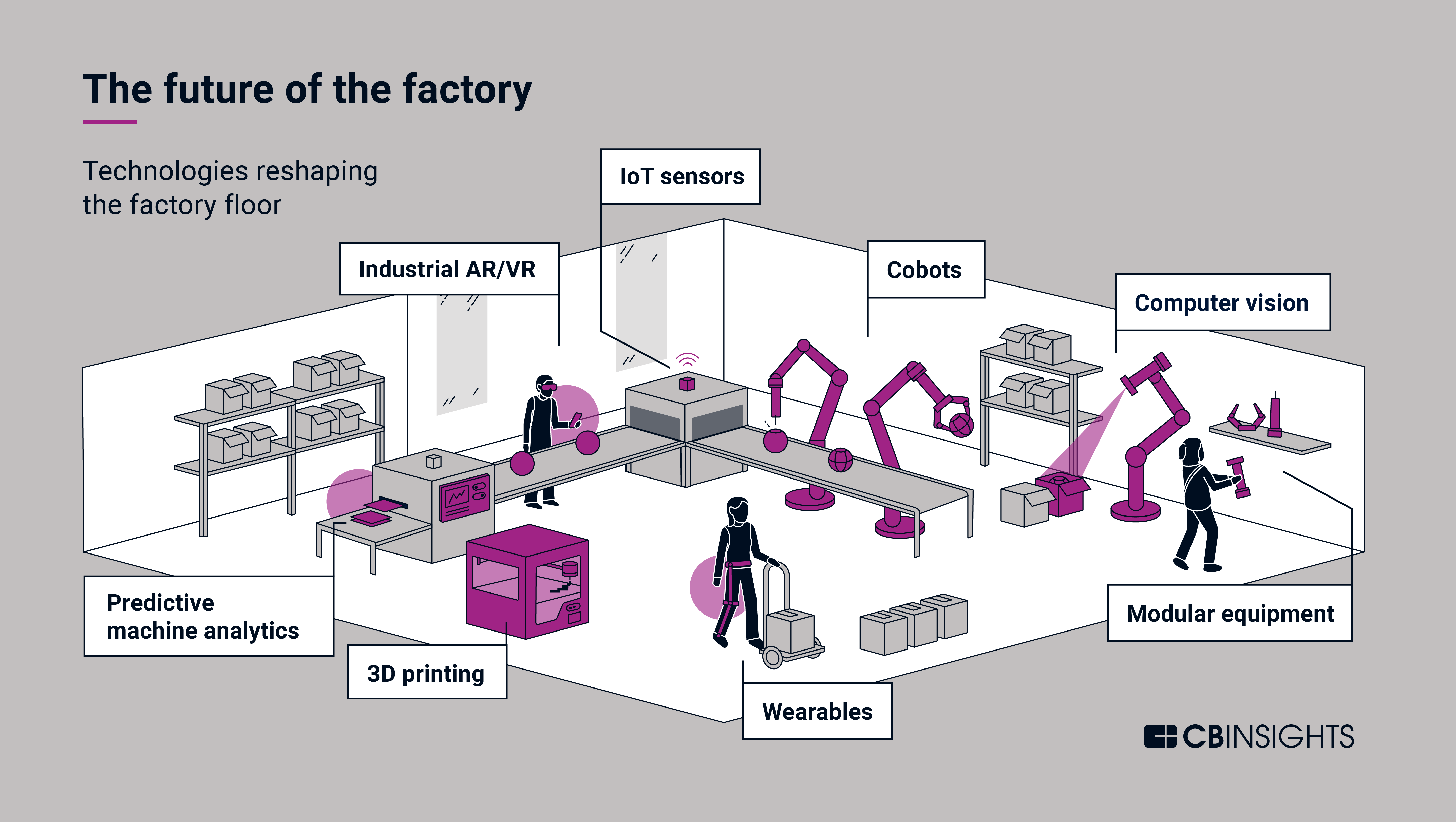
3. Advanced Robotics and Automation:
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Cobots are designed to work alongside human operators, enhancing productivity and safety in manufacturing environments. They perform repetitive or dangerous tasks, freeing up human workers for more complex and value-added activities.
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): AGVs are autonomous vehicles used for material handling within factories. They navigate autonomously, reducing manual labor and improving efficiency in logistics and transportation.
- 3D Printing: Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is revolutionizing production by enabling the creation of complex and customized products on demand. This technology allows for faster prototyping, reduced waste, and personalized manufacturing.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being integrated into various aspects of manufacturing, from quality control and process optimization to predictive maintenance and robot control.
Benefits:
- Increased Productivity: Automation reduces manual labor, allowing for faster production cycles and higher output.
- Improved Safety: Robots and automated systems can perform dangerous or repetitive tasks, reducing workplace injuries.
- Enhanced Flexibility: Automated systems are easily adaptable to changing production needs, allowing for greater flexibility in manufacturing.
- Reduced Costs: Automation can lead to significant cost savings by reducing labor costs, material waste, and downtime.
4. Advanced Materials and Manufacturing Processes:
- Nanotechnology: The manipulation of materials at the nanoscale is leading to the development of new materials with enhanced properties, such as strength, conductivity, and heat resistance.
- Lightweight Materials: Manufacturers are increasingly using lightweight materials like composites and advanced alloys to reduce weight, improve fuel efficiency, and enhance product performance.
- Advanced Manufacturing Processes: Technologies like laser cutting, waterjet cutting, and additive manufacturing are enabling the creation of complex and intricate products with higher precision and efficiency.
Benefits:
- Improved Performance: Advanced materials and processes lead to products with superior strength, durability, and functionality.
- Reduced Weight: Lightweight materials improve fuel efficiency and reduce transportation costs.
- Enhanced Durability: Advanced materials and manufacturing processes result in products that are more resistant to wear and tear.
- Increased Design Flexibility: New technologies allow for greater design freedom, enabling the creation of products with complex geometries.
5. Personalized and Mass Customization:
- Customer-Centric Manufacturing: Manufacturers are shifting their focus towards meeting individual customer needs, offering personalized products and services.
- Mass Customization: Technology enables the production of customized goods on a large scale, allowing manufacturers to offer tailored products while maintaining cost efficiency.
- Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Models: Manufacturers are increasingly selling directly to consumers, bypassing traditional retail channels and gaining valuable customer insights.
Benefits:
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Personalized products meet specific customer needs, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
- New Revenue Streams: Mass customization allows manufacturers to offer unique products and tap into new markets.
- Improved Customer Relationships: D2C models enable direct communication with customers, fostering stronger relationships and loyalty.
6. The Workforce of the Future:
- Upskilling and Reskilling: Manufacturers are investing in training programs to equip their workforce with the skills needed to operate in a digital and automated environment.
- Attracting and Retaining Talent: Companies are focusing on creating attractive work environments and offering competitive benefits to attract and retain skilled employees.
- Collaboration with Educational Institutions: Manufacturers are partnering with universities and vocational schools to develop talent pipelines and bridge the skills gap.
Benefits:
- Improved Productivity: A skilled and adaptable workforce is essential for maximizing the benefits of automation and digital technologies.
- Enhanced Innovation: A workforce with diverse skills and knowledge drives innovation and creativity.
- Increased Competitiveness: Investing in human capital helps manufacturers stay ahead of the competition in a rapidly evolving industry.
7. Supply Chain Resilience:
- Agile Supply Chains: Manufacturers are adopting agile supply chain models to respond quickly to disruptions and market fluctuations. This involves building flexible and resilient networks that can adapt to changing conditions.
- Nearshoring and Reshoring: Some manufacturers are bringing production back to their home countries or relocating to nearby regions to reduce supply chain risk and improve control over production processes.
- Supply Chain Visibility: Real-time data and analytics provide insights into supply chain operations, allowing manufacturers to identify potential disruptions and take proactive measures.
Benefits:
- Reduced Risk: Resilient supply chains minimize the impact of disruptions, ensuring continued production and delivery.
- Improved Efficiency: Agile supply chains optimize resource allocation and streamline logistics, leading to cost savings.
- Enhanced Control: Nearshoring and reshoring give manufacturers greater control over production processes and quality.
8. The Rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Connected Manufacturing:
- Smart Sensors and Data Analytics: IoT devices and smart sensors collect real-time data on production processes, equipment performance, and product quality, enabling manufacturers to optimize operations and identify potential issues.
- Predictive Maintenance: Data analytics and AI algorithms enable manufacturers to predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance proactively, reducing downtime and improving efficiency.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: IoT enables manufacturers to remotely monitor and control production processes, allowing for greater flexibility and responsiveness.
Benefits:
- Improved Efficiency: Real-time data and analytics optimize production processes, reduce waste, and increase productivity.
- Reduced Downtime: Predictive maintenance minimizes equipment failures and downtime, improving operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Safety: Remote monitoring and control allow for early detection of potential hazards, improving safety in manufacturing environments.
FAQs:
Q: What are the key drivers of these trends in manufacturing?
A: The key drivers of these trends include technological advancements, evolving consumer demands, the need for sustainability, and increasing competition.
Q: How can manufacturers prepare for these changes?
A: Manufacturers should invest in digital transformation, embrace sustainable practices, adopt advanced robotics and automation, and develop a skilled workforce. They should also focus on building resilient supply chains and leveraging the power of the Internet of Things.
Q: What are the potential challenges associated with these trends?
A: Challenges include the cost of implementing new technologies, the need for skilled labor, and the potential for job displacement.
Tips:
- Embrace a Digital Mindset: Invest in data analytics, cloud computing, and other digital technologies to optimize operations and gain competitive advantage.
- Prioritize Sustainability: Adopt sustainable practices throughout the value chain, from sourcing materials to reducing waste and emissions.
- Invest in Automation: Explore advanced robotics and automation solutions to enhance productivity, improve safety, and reduce costs.
- Upskill Your Workforce: Invest in training programs to equip your employees with the skills needed for a digital and automated environment.
- Build a Resilient Supply Chain: Develop agile and flexible supply chain networks to minimize disruptions and ensure continuity of operations.
- Leverage the Power of the Internet of Things: Integrate IoT devices and smart sensors to collect real-time data and optimize production processes.
Conclusion:
The trends in manufacturing industry 2025 are ushering in a new era of innovation, efficiency, and sustainability. By embracing these trends, manufacturers can position themselves for success in a rapidly evolving industry landscape. The future of manufacturing is digital, sustainable, and human-centered, requiring a strategic and forward-looking approach to navigate the challenges and capitalize on the opportunities ahead.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shaping the Future: Trends in Manufacturing Industry 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!