Shaping the Future: Trends That Will Define 2025
Related Articles: Shaping the Future: Trends That Will Define 2025
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Shaping the Future: Trends That Will Define 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Shaping the Future: Trends That Will Define 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Shaping the Future: Trends That Will Define 2025
- 3.1 The Catalysts of Change
- 3.2 The Defining Trends Benders
- 3.2.1 1. The Rise of AI and Automation
- 3.2.2 2. The Metaverse and Immersive Experiences
- 3.2.3 3. The Rise of the Sharing Economy
- 3.2.4 4. Sustainable Development and Circular Economy
- 3.2.5 5. The Future of Work: Remote Work and Flexibility
- 3.2.6 6. Data-Driven Decision Making and Personalized Experiences
- 3.2.7 7. The Rise of Digital Health and Wellness
- 3.2.8 8. The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity
- 3.3 Related Searches:
- 3.3.9 1. Future of Technology Trends
- 3.3.10 2. Future of Work Trends
- 3.3.11 3. Future of Education Trends
- 3.3.12 4. Future of Marketing Trends
- 3.3.13 5. Future of Healthcare Trends
- 3.3.14 6. Future of Finance Trends
- 3.3.15 7. Future of Sustainability Trends
- 3.3.16 8. Future of Cities Trends
- 3.4 FAQs:
- 4 Closure
Shaping the Future: Trends That Will Define 2025

The year 2025 feels like a distant horizon, yet it’s rapidly approaching. This period will be marked by a convergence of technological advancements, societal shifts, and evolving consumer behaviors, creating a landscape unlike anything we’ve seen before. Identifying and understanding the trends benders of 2025 is crucial for individuals, businesses, and societies to navigate this dynamic future effectively.
This article delves into the key trends benders that will shape 2025, exploring their impact across various domains. We will examine the forces driving these trends, their potential benefits, and the challenges they present. Understanding these shifts will empower individuals, organizations, and policymakers to anticipate, adapt, and even influence the future.
The Catalysts of Change
Several fundamental forces are converging to create the landscape of 2025, acting as the driving engines behind the trends benders. These include:
- Technological Acceleration: The rapid pace of technological innovation, particularly in areas like artificial intelligence (AI), quantum computing, and biotechnology, is transforming industries and daily life. This acceleration fuels the development of new solutions, products, and services, redefining how we work, interact, and live.
- Demographic Shifts: The world is undergoing significant demographic changes, with aging populations in developed nations and burgeoning youth populations in emerging economies. These shifts impact consumer preferences, workforce dynamics, and societal priorities, creating new opportunities and challenges.
- Climate Change: The undeniable reality of climate change is forcing a global re-evaluation of our relationship with the environment. Sustainability, renewable energy, and circular economy models are becoming increasingly important, driving innovation and influencing consumer choices.
- Globalization and Connectivity: The interconnectedness of the world continues to grow, with increased cross-border trade, communication, and cultural exchange. This interconnectedness presents opportunities for global collaboration but also raises challenges related to geopolitical tensions, cybersecurity, and ethical considerations.
These forces are intertwined, amplifying each other’s impact and shaping the future in complex and multifaceted ways. Understanding their interplay is key to comprehending the trends benders that will define 2025.
The Defining Trends Benders
The trends benders of 2025 are not isolated phenomena but rather interconnected forces that will shape the future landscape. These trends encompass various domains, from technology and business to society and culture.
1. The Rise of AI and Automation
AI is rapidly evolving, becoming increasingly sophisticated and accessible. This is leading to a wave of automation across various industries, from manufacturing and logistics to customer service and healthcare.
-
Impact:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: AI-powered automation can streamline processes, reduce human error, and boost productivity, leading to cost savings and faster turnaround times.
- Job Displacement and Reskilling: While automation creates new jobs in AI development and data science, it also displaces workers in traditional roles. This necessitates reskilling and upskilling programs to equip the workforce for the future.
- Personalized Experiences: AI can personalize user experiences, tailoring recommendations, services, and content to individual preferences. This can enhance customer satisfaction and create more engaging interactions.
-
Examples:
- Self-driving cars: AI is transforming the automotive industry with the development of self-driving vehicles, promising increased safety, reduced traffic congestion, and new mobility options.
- Chatbots and virtual assistants: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are becoming increasingly common in customer service, providing instant support and personalized assistance.
- Precision medicine: AI is revolutionizing healthcare, enabling personalized treatment plans based on individual genetic profiles and medical histories.
2. The Metaverse and Immersive Experiences
The metaverse is an evolving concept, envisioning a persistent, shared virtual space where users can interact, work, and play. It encompasses virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) technologies, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds.
-
Impact:
- Enhanced Social Connection: The metaverse can foster new forms of social interaction and community building, enabling users to connect with others regardless of physical location.
- New Business Models: The metaverse presents opportunities for businesses to create immersive experiences, offer virtual goods and services, and develop new revenue streams.
- Education and Training: VR and AR technologies can revolutionize education and training by providing immersive, interactive learning experiences.
-
Examples:
- Virtual worlds: Companies like Meta (formerly Facebook) are developing virtual worlds where users can socialize, play games, and attend virtual events.
- AR shopping experiences: Retailers are using AR to create interactive shopping experiences, allowing customers to visualize products in their homes before purchasing.
- VR training simulations: Industries like healthcare and manufacturing are utilizing VR to create realistic training simulations, enhancing employee skills and safety.
3. The Rise of the Sharing Economy
The sharing economy, fueled by platforms like Airbnb, Uber, and TaskRabbit, continues to grow, disrupting traditional industries and redefining ownership models.
-
Impact:
- Access over Ownership: The sharing economy emphasizes access to goods and services rather than ownership, enabling individuals to utilize resources more efficiently and reduce consumption.
- Empowerment of Individuals: Platforms like Airbnb and Uber empower individuals to generate income by sharing their assets and skills, creating new economic opportunities.
- Sustainability and Resource Optimization: Sharing economy models can promote sustainability by reducing waste and maximizing the utilization of existing resources.
-
Examples:
- Ride-hailing services: Uber and Lyft have revolutionized transportation, providing on-demand rides and reducing car ownership.
- Collaborative consumption: Platforms like Airbnb and Couchsurfing enable individuals to share their homes and spaces with travelers, fostering cultural exchange and reducing tourism’s environmental impact.
- Gig economy: Platforms like Upwork and Fiverr connect freelancers with clients, offering flexible work opportunities and access to a global talent pool.
4. Sustainable Development and Circular Economy
The growing awareness of climate change and resource scarcity is driving a shift towards sustainable practices and circular economy models.
-
Impact:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Sustainable practices aim to minimize environmental damage, conserve resources, and reduce waste.
- Economic Opportunities: Circular economy models create new business opportunities, focusing on reusing, repairing, and recycling materials to reduce resource extraction and waste.
- Societal Change: Sustainable development requires a shift in societal values, promoting responsible consumption and encouraging individuals to make environmentally conscious choices.
-
Examples:
- Renewable energy: The transition to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power is crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change.
- Circular fashion: Brands are embracing circular fashion practices, focusing on durable, repairable, and recyclable clothing to reduce waste and minimize environmental impact.
- Sustainable agriculture: Practices like organic farming, agroforestry, and regenerative agriculture promote soil health, biodiversity, and sustainable food production.
5. The Future of Work: Remote Work and Flexibility
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work, transforming how and where we work. This trend is likely to continue, leading to increased flexibility and a more decentralized workforce.
-
Impact:
- Increased Productivity and Employee Satisfaction: Remote work can enhance productivity by reducing commute times and offering greater flexibility, leading to higher employee satisfaction and retention.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Remote work can broaden the talent pool, enabling companies to hire individuals from diverse backgrounds and locations, fostering greater inclusivity.
- Economic Impact: Remote work can boost local economies in areas where remote workers choose to live, as they contribute to local businesses and services.
-
Examples:
- Remote-first companies: Many companies have adopted a remote-first or hybrid work model, offering employees the flexibility to work from home or from various locations.
- Virtual collaboration tools: Platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Slack facilitate virtual collaboration and communication, enabling remote teams to work effectively.
- Digital nomads: The rise of remote work has also led to the growth of the digital nomad lifestyle, with individuals traveling and working remotely from various locations around the world.
6. Data-Driven Decision Making and Personalized Experiences
The explosion of data is transforming how we make decisions, with organizations leveraging data analytics to gain insights and optimize operations. This trend is leading to personalized experiences across various domains, from e-commerce to healthcare.
-
Impact:
- Improved Efficiency and Innovation: Data analytics can identify patterns and trends, enabling organizations to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and drive innovation.
- Personalized Experiences: Data can be used to create personalized experiences, tailoring products, services, and recommendations to individual preferences.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of data raises ethical concerns about privacy, security, and potential bias in algorithms.
-
Examples:
- E-commerce personalization: Online retailers use data to personalize product recommendations and marketing messages, tailoring the shopping experience to individual preferences.
- Healthcare analytics: Hospitals and healthcare providers use data analytics to improve patient care, predict disease outbreaks, and optimize resource allocation.
- Smart cities: Cities are leveraging data to optimize traffic flow, manage energy consumption, and improve public safety.
7. The Rise of Digital Health and Wellness
Technology is revolutionizing healthcare, with the emergence of digital health tools and platforms that empower individuals to take control of their health and well-being.
-
Impact:
- Improved Access to Healthcare: Digital health tools can expand access to healthcare services, particularly in remote areas and underserved communities.
- Personalized Health Management: Wearable devices and mobile apps can track health data, provide personalized insights, and support individuals in making healthy lifestyle choices.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Telemedicine and remote patient monitoring technologies enable healthcare professionals to provide care remotely, improving patient convenience and reducing healthcare costs.
-
Examples:
- Wearable health trackers: Devices like Fitbits and Apple Watches track activity levels, sleep patterns, and other health metrics, providing insights and motivation for healthier living.
- Telemedicine platforms: Platforms like Teladoc and MDLive connect patients with healthcare providers remotely via video conferencing, offering convenient and accessible healthcare services.
- Digital therapeutics: Mobile apps and digital platforms are being developed to treat mental health conditions, providing personalized therapy and support.
8. The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity
As we become increasingly reliant on technology, cybersecurity becomes paramount. Protecting data and systems from cyberattacks is crucial for individuals, businesses, and governments.
-
Impact:
- Increased Vulnerability: The interconnectedness of systems and the growing reliance on digital infrastructure increase vulnerability to cyberattacks.
- Economic and Societal Consequences: Cyberattacks can disrupt businesses, steal sensitive data, and cause significant financial and reputational damage.
- Innovation in Cybersecurity: The need to protect against cyber threats is driving innovation in cybersecurity technologies, such as advanced threat detection and response systems.
-
Examples:
- Data breaches: Companies and organizations are increasingly targeted by cybercriminals seeking to steal sensitive data, such as financial information or personal records.
- Ransomware attacks: Ransomware attacks encrypt data and demand payment for its release, disrupting business operations and causing significant financial losses.
- Nation-state hacking: Governments and state-sponsored actors engage in cyber espionage and cyberwarfare, targeting critical infrastructure and sensitive information.
Related Searches:
1. Future of Technology Trends
The future of technology is characterized by exponential growth and innovation, driven by advancements in AI, quantum computing, biotechnology, and other emerging fields. These trends will reshape industries, create new opportunities, and redefine how we live, work, and interact with the world.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI is rapidly evolving, becoming increasingly sophisticated and accessible. This is leading to a wave of automation across various industries, from manufacturing and logistics to customer service and healthcare. AI is also driving innovation in areas like personalized medicine, self-driving cars, and smart homes.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize various fields, from drug discovery and materials science to cryptography and financial modeling. This technology leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to perform complex calculations that are impossible for classical computers.
- Biotechnology: Advancements in biotechnology are leading to breakthroughs in areas like gene editing, personalized medicine, and synthetic biology. These technologies have the potential to transform healthcare, agriculture, and other industries.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT refers to the interconnectedness of devices and objects through the internet, enabling them to collect and exchange data. This trend is leading to the development of smart homes, smart cities, and other connected ecosystems.
2. Future of Work Trends
The future of work is characterized by increasing automation, globalization, and the rise of the gig economy. These trends are transforming how we work, where we work, and the skills we need to succeed.
- Remote Work and Flexibility: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work, transforming how and where we work. This trend is likely to continue, leading to increased flexibility and a more decentralized workforce.
- Automation and Job Displacement: AI and automation are transforming various industries, leading to job displacement in traditional roles. This necessitates reskilling and upskilling programs to equip the workforce for the future.
- Gig Economy and Freelancing: The gig economy is growing rapidly, offering flexible work opportunities and access to a global talent pool. Platforms like Upwork and Fiverr connect freelancers with clients, providing alternative employment options.
- Skills Gap and Future-Proofing: The future of work requires individuals to adapt and develop in-demand skills, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and digital literacy. Education and training programs need to evolve to meet the changing needs of the workforce.
3. Future of Education Trends
The future of education is characterized by personalized learning, technology-driven classrooms, and lifelong learning. These trends are transforming how we learn, what we learn, and where we learn.
- Personalized Learning: Education is shifting towards personalized learning experiences, tailored to individual needs and learning styles. This approach leverages technology and data analytics to provide customized instruction and support.
- Technology in the Classroom: Technology is playing an increasingly important role in education, with classrooms becoming more interactive and engaging. Virtual reality, augmented reality, and online learning platforms are transforming the learning experience.
- Lifelong Learning: In a rapidly changing world, lifelong learning is essential for individuals to stay competitive and adapt to new challenges. This trend emphasizes continuous learning and upskilling throughout one’s career.
- STEM Education: STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education is becoming increasingly important, as these fields are driving innovation and economic growth.
4. Future of Marketing Trends
The future of marketing is characterized by personalization, data-driven strategies, and the rise of new channels. These trends are transforming how businesses connect with customers, build relationships, and drive sales.
- Personalized Marketing: Data analytics and AI are enabling marketers to personalize their messages and experiences, tailoring them to individual preferences and behaviors.
- Content Marketing: Content marketing is becoming increasingly important, as businesses strive to create valuable and engaging content that attracts and retains customers.
- Social Media Marketing: Social media platforms are evolving rapidly, offering new opportunities for businesses to reach and engage with their target audiences.
- Influencer Marketing: Influencer marketing is gaining traction, with businesses partnering with influencers to reach their target audiences and promote their products or services.
5. Future of Healthcare Trends
The future of healthcare is characterized by personalized medicine, digital health tools, and a focus on preventive care. These trends are transforming how we diagnose, treat, and manage health conditions.
- Personalized Medicine: Advancements in genomics, AI, and other technologies are enabling personalized medicine, tailoring treatment plans to individual genetic profiles and medical histories.
- Digital Health Tools: Wearable devices, mobile apps, and telemedicine platforms are empowering individuals to take control of their health and well-being.
- Preventive Care: The focus is shifting from treating illness to preventing it, with a greater emphasis on healthy lifestyles, early detection, and personalized prevention strategies.
- Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: AI is revolutionizing healthcare, enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and the development of new drugs and therapies.
6. Future of Finance Trends
The future of finance is characterized by digitalization, fintech innovation, and a focus on financial inclusion. These trends are transforming how we manage our money, invest, and access financial services.
- Fintech Innovation: Fintech companies are disrupting traditional financial institutions, offering innovative products and services, such as mobile payments, peer-to-peer lending, and robo-advisors.
- Digital Banking: Digital banking is becoming increasingly popular, with customers utilizing mobile apps and online platforms to manage their finances, make payments, and access financial services.
- Cryptocurrency and Blockchain: Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology are revolutionizing finance, offering decentralized and secure ways to manage and transfer funds.
- Financial Inclusion: The goal of financial inclusion is to provide access to financial services for everyone, regardless of income or location. This trend is driven by the need to empower individuals and promote economic growth.
7. Future of Sustainability Trends
The future of sustainability is characterized by a shift towards circular economy models, renewable energy sources, and sustainable practices across all industries. These trends are essential for mitigating climate change, conserving resources, and creating a more sustainable future.
- Circular Economy: Circular economy models focus on reusing, repairing, and recycling materials to reduce waste and minimize resource extraction.
- Renewable Energy: The transition to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power is crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Practices like organic farming, agroforestry, and regenerative agriculture promote soil health, biodiversity, and sustainable food production.
- Green Technology: Green technology encompasses technologies and innovations that aim to reduce environmental impact and promote sustainability.
8. Future of Cities Trends
The future of cities is characterized by urbanization, smart city technologies, and a focus on sustainability and livability. These trends are transforming how we design, build, and manage cities.
- Urbanization: The global population is becoming increasingly urbanized, with more people living in cities than ever before. This trend is driving the need for sustainable and resilient cities.
- Smart City Technologies: Smart cities leverage technology to improve efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life. This includes using sensors, data analytics, and AI to optimize traffic flow, manage energy consumption, and enhance public safety.
- Sustainable Urban Development: Sustainable urban development prioritizes environmental protection, resource efficiency, and social equity. This includes promoting green spaces, reducing carbon emissions, and creating equitable and inclusive cities.
- Urban Mobility: Sustainable transportation solutions, such as public transit, cycling infrastructure, and electric vehicles, are essential for reducing congestion and improving air quality in cities.
FAQs:
- What are the key drivers of these trends?
The key drivers of these trends are technological acceleration, demographic

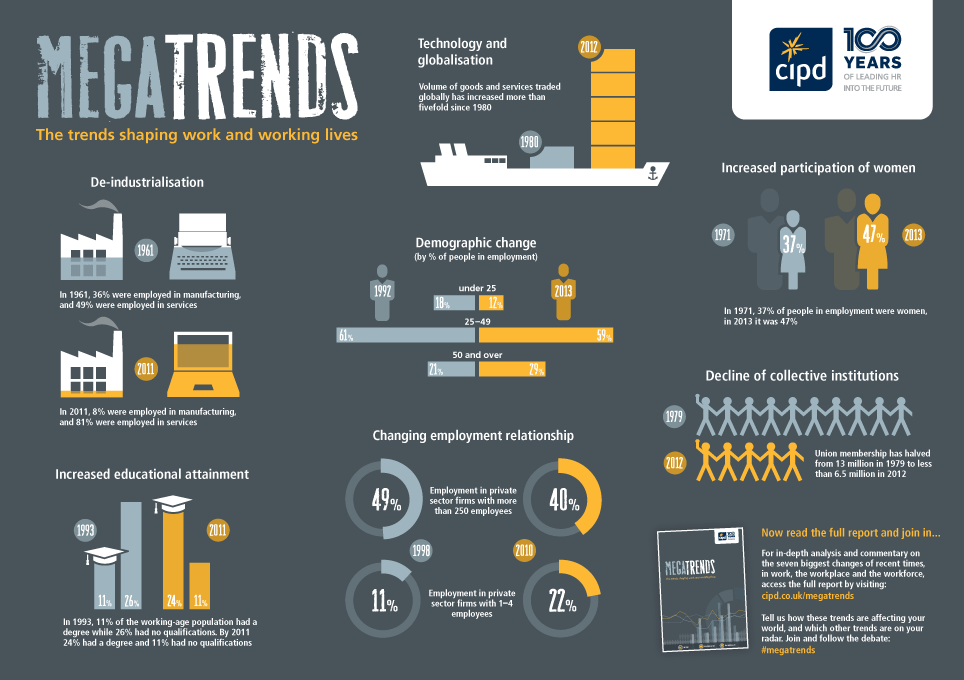






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shaping the Future: Trends That Will Define 2025. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!