The Evolving Landscape of MIS: Key Technological Trends Shaping the Future
Related Articles: The Evolving Landscape of MIS: Key Technological Trends Shaping the Future
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Evolving Landscape of MIS: Key Technological Trends Shaping the Future. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Evolving Landscape of MIS: Key Technological Trends Shaping the Future

The field of Management Information Systems (MIS) is in a constant state of flux, driven by the relentless pace of technological innovation. Understanding and adapting to these emerging trends is crucial for organizations seeking to remain competitive and leverage the full potential of information technology. This article delves into eight key trends shaping the future of MIS, offering insights into their significance and potential impact.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are no longer futuristic concepts; they are actively transforming MIS practices. From automating routine tasks to predicting future trends, AI and ML are revolutionizing how organizations collect, analyze, and utilize data.
Applications in MIS:
- Predictive Analytics: AI models can analyze historical data to identify patterns and forecast future outcomes, enabling organizations to make informed decisions about resource allocation, inventory management, and customer behavior.
- Process Automation: AI-powered tools can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up MIS professionals to focus on more strategic initiatives. This includes tasks like data entry, report generation, and system maintenance.
- Personalized Customer Experiences: AI can personalize customer interactions, providing tailored recommendations and support based on individual preferences and past interactions.
Benefits:
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: AI and ML automation can streamline processes, reduce human error, and increase productivity.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: AI-driven insights provide a more comprehensive understanding of data, allowing organizations to make better-informed decisions.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations leveraging AI and ML gain a competitive edge by optimizing operations, improving customer experiences, and identifying new opportunities.
2. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has become the cornerstone of modern MIS, offering scalable and cost-effective solutions for data storage, processing, and application delivery. This shift allows organizations to access computing resources on demand, without the need for significant upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure.
Types of Cloud Services:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides access to computing resources like servers, storage, and networking.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform for developing and deploying applications, including tools and services for database management, application development, and testing.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for local installation and maintenance.
Benefits:
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud computing allows organizations to scale their resources up or down as needed, adapting to fluctuating demands.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go pricing models reduce upfront investment and offer greater cost control.
- Accessibility and Collaboration: Cloud-based systems provide remote access and facilitate collaboration among team members.
3. Big Data and Analytics
Big data and analytics are transforming how organizations extract valuable insights from massive datasets. The ability to collect, store, and analyze vast amounts of data opens new avenues for understanding customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency.
Types of Big Data Analytics:
- Descriptive Analytics: Focuses on understanding past events and trends.
- Predictive Analytics: Uses historical data to forecast future outcomes.
- Prescriptive Analytics: Identifies optimal actions based on data analysis.
Benefits:
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Big data analytics provides valuable insights that support informed decision-making across all aspects of an organization.
- Improved Customer Experience: Analyzing customer data enables businesses to personalize experiences, enhance customer service, and develop targeted marketing campaigns.
- Operational Efficiency: Big data can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in operations, leading to improved performance and cost optimization.
4. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a decentralized, secure, and transparent ledger system that holds immense potential for revolutionizing MIS processes. Its immutability and security features make it ideal for managing sensitive data, tracking supply chains, and securing transactions.
Applications in MIS:
- Data Security and Integrity: Blockchain ensures data integrity and immutability, making it a secure platform for storing and managing sensitive information.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track products throughout the supply chain, improving transparency, accountability, and efficiency.
- Financial Transactions: Blockchain facilitates secure and transparent financial transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and enhancing trust.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Security: Blockchain’s decentralized nature and cryptographic encryption make it highly secure against data breaches and manipulation.
- Increased Transparency: All transactions are recorded on the blockchain, providing a transparent and auditable record of all activities.
- Improved Efficiency: Blockchain streamlines processes, reduces the need for intermediaries, and accelerates transaction times.
5. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the interconnected network of devices, sensors, and machines that collect and exchange data. This interconnectedness creates a vast network of data sources that can be leveraged by MIS systems to enhance operations, improve decision-making, and create new business opportunities.
Applications in MIS:
- Real-time Monitoring and Control: IoT sensors provide real-time data on equipment performance, environmental conditions, and customer behavior.
- Predictive Maintenance: IoT data can be used to predict equipment failures and schedule preventative maintenance, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Smart Buildings and Cities: IoT enables smart building systems that optimize energy consumption, enhance security, and improve occupant comfort.
Benefits:
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: IoT data provides real-time insights that optimize operations and improve efficiency.
- Enhanced Customer Experiences: IoT devices can personalize customer interactions, provide real-time support, and enhance product usability.
- New Business Opportunities: IoT data can create new business opportunities by developing innovative products and services.
6. Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is becoming increasingly crucial in the digital age, as organizations face growing threats from cyberattacks. MIS professionals play a critical role in safeguarding sensitive data, protecting systems, and mitigating cyber risks.
Key Cybersecurity Concerns:
- Data Breaches: Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting sensitive data, such as personal information, financial records, and intellectual property.
- Malware and Ransomware: Malware can disrupt operations, steal data, and hold systems hostage through ransomware attacks.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Cybercriminals use social engineering tactics to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or granting access to systems.
Importance in MIS:
- Protecting Data and Systems: MIS professionals implement security measures to protect sensitive data and ensure system integrity.
- Developing Security Policies: Organizations need comprehensive cybersecurity policies that define roles, responsibilities, and procedures for handling sensitive data.
- Investing in Security Technologies: MIS professionals use advanced security tools, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption, to mitigate cyber risks.
7. Edge Computing
Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and improving responsiveness. This approach allows organizations to process data in real-time at the edge of the network, eliminating the need to send data to a central data center.
Applications in MIS:
- Real-time Data Analysis: Edge computing enables real-time analysis of data generated by IoT devices, allowing for immediate decision-making.
- Autonomous Systems: Edge computing supports the development of autonomous systems, such as self-driving cars and robots, by enabling real-time decision-making and control.
- Improved Network Performance: Edge computing reduces latency and improves network performance by processing data closer to the user.
Benefits:
- Reduced Latency: Edge computing minimizes the time it takes to process data, improving responsiveness and enhancing user experience.
- Improved Scalability and Reliability: Edge computing distributes processing power across the network, improving scalability and reliability.
- Enhanced Security: Processing data at the edge reduces the need to transmit sensitive data over the network, enhancing security.
8. Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is a rapidly developing field that holds the potential to revolutionize MIS by solving complex problems that are intractable for traditional computers. This technology utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations at speeds far exceeding those of classical computers.
Applications in MIS:
- Drug Discovery and Materials Science: Quantum computers can accelerate drug discovery and materials research by simulating complex molecular interactions.
- Financial Modeling: Quantum computing can optimize financial models, enabling better risk management and investment strategies.
- Artificial Intelligence: Quantum computing can enhance AI algorithms, leading to more efficient and powerful machine learning models.
Benefits:
- Unprecedented Processing Power: Quantum computers offer exponential speedups for certain types of calculations, opening new possibilities for data analysis and problem-solving.
- Breakthrough Innovations: Quantum computing has the potential to drive breakthroughs in various fields, including medicine, materials science, and artificial intelligence.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that embrace quantum computing will gain a significant competitive advantage by leveraging its unique capabilities.
Related Searches
- MIS Trends 2025: Exploring the future of MIS, including emerging technologies and their impact on business operations.
- Future of MIS: Examining the long-term trends and technological advancements shaping the field of MIS.
- Technology Trends in Business: Analyzing the broader impact of technology on business strategies, operations, and customer interactions.
- Digital Transformation in MIS: Understanding how digital technologies are transforming MIS practices and creating new opportunities.
- Emerging Technologies in MIS: Exploring cutting-edge technologies like quantum computing, blockchain, and AI that are poised to revolutionize MIS.
- Impact of Technology on MIS: Assessing the influence of technology on MIS roles, skills, and responsibilities.
- MIS Career Paths: Examining career opportunities in MIS, including roles in data analytics, cybersecurity, and cloud computing.
- MIS Education and Training: Exploring educational and training programs for MIS professionals, covering topics like AI, big data, and cybersecurity.
FAQs
-
What are the most important MIS trends for organizations to focus on?
- Organizations should prioritize AI and ML, cloud computing, big data and analytics, cybersecurity, and IoT. These technologies offer significant opportunities to improve efficiency, enhance decision-making, and gain a competitive advantage.
-
How can organizations prepare for the future of MIS?
- Organizations should invest in training and development programs for their MIS professionals, adopt agile methodologies, and embrace a culture of innovation. They should also actively research and explore emerging technologies to stay ahead of the curve.
-
What are the potential challenges of implementing these MIS trends?
- Challenges include the need for skilled professionals, data privacy concerns, security risks, and the potential for disruption to existing processes. Organizations need to carefully plan and manage the implementation of these trends to mitigate these challenges.
Tips
- Embrace a Data-Driven Culture: Encourage data-driven decision-making throughout the organization.
- Invest in Talent Development: Develop and retain skilled MIS professionals who can navigate the evolving technological landscape.
- Stay Informed about Emerging Technologies: Continuously research and explore new technologies to identify opportunities and potential disruptions.
- Prioritize Cybersecurity: Implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and systems from cyber threats.
- Foster Collaboration and Innovation: Encourage collaboration between MIS professionals and other departments to identify innovative solutions.
Conclusion
The future of MIS is shaped by a dynamic interplay of technological advancements and evolving business needs. Understanding and adapting to these trends is essential for organizations seeking to leverage the power of information technology to achieve their strategic objectives. By embracing these trends, organizations can unlock new opportunities for efficiency, innovation, and competitive advantage in the digital age. The MIS field is constantly evolving, and staying informed about these trends is crucial for success in the ever-changing world of information technology.




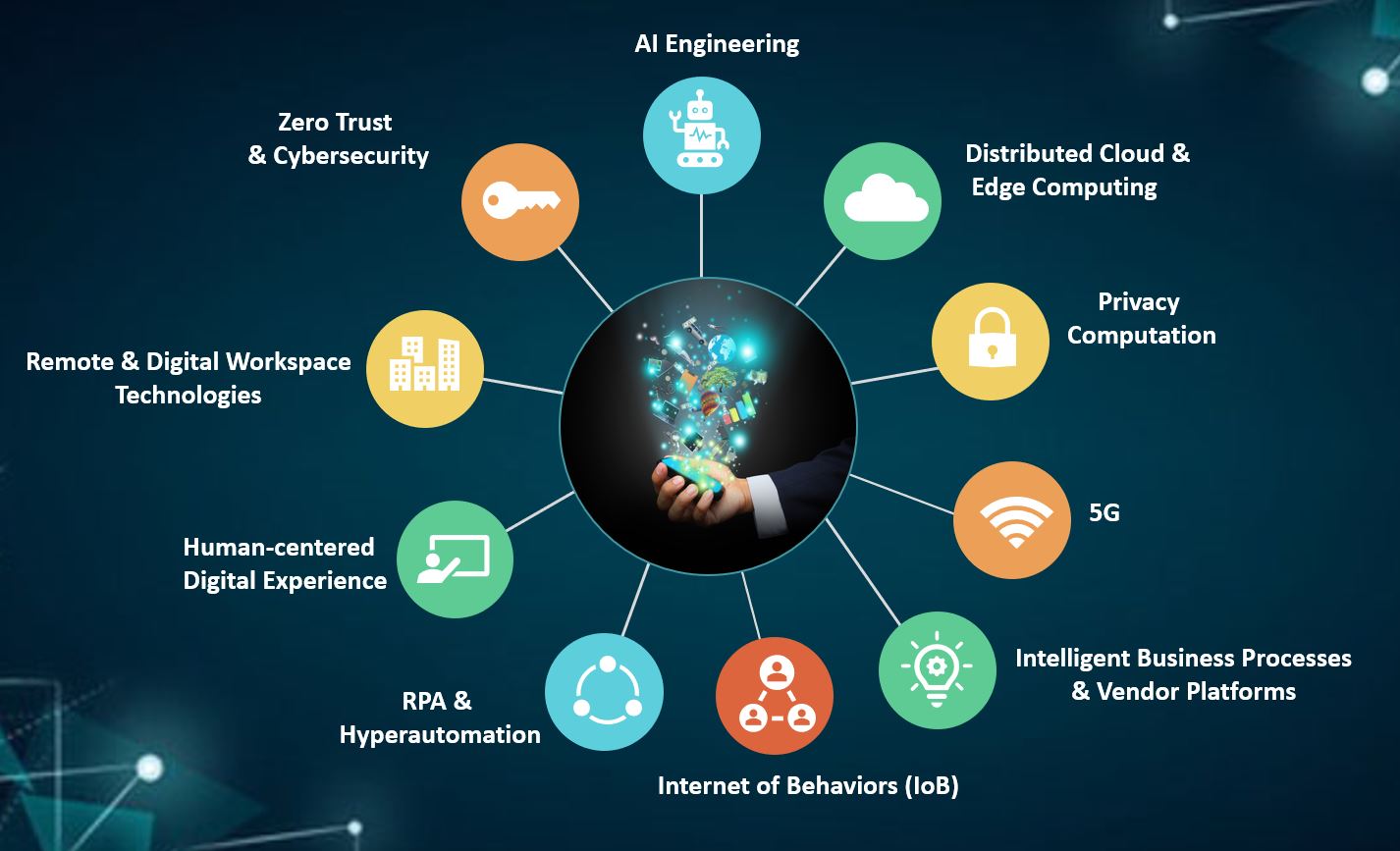


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Evolving Landscape of MIS: Key Technological Trends Shaping the Future. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!