The Shifting Landscape of Puberty: Exploring Secular Trends in 2025
Related Articles: The Shifting Landscape of Puberty: Exploring Secular Trends in 2025
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Landscape of Puberty: Exploring Secular Trends in 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Shifting Landscape of Puberty: Exploring Secular Trends in 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Shifting Landscape of Puberty: Exploring Secular Trends in 2025
- 3.1 Understanding Secular Trends in Puberty
- 3.2 Implications of Secular Trends in Puberty
- 3.3 Secular Trends in Puberty: A Look Ahead to 2025
- 3.4 Related Searches:
- 3.5 FAQs:
- 3.6 Tips:
- 3.7 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
The Shifting Landscape of Puberty: Exploring Secular Trends in 2025

The process of puberty, a period of rapid physical and hormonal changes leading to sexual maturity, has long been considered a universal human experience. However, recent decades have witnessed a gradual but significant shift in the timing and progression of this developmental stage, a phenomenon known as secular trends in puberty. This article delves into the complexities of these trends, examining their potential causes, implications, and what we can expect in 2025 and beyond.
Understanding Secular Trends in Puberty
Secular trends in puberty refer to long-term, gradual changes in the age of puberty onset and progression observed across generations within a population. These trends are not driven by genetic factors but rather by environmental and lifestyle influences. While the exact mechanisms are still under investigation, several contributing factors have been identified.
1. Nutrition and Body Mass Index (BMI): Increased access to calorie-rich diets and sedentary lifestyles have led to higher BMIs in children, potentially accelerating puberty onset. Studies have shown a correlation between early puberty and increased BMI, particularly in girls.
2. Endocrine Disruptors: Chemicals found in everyday products like plastics, pesticides, and cosmetics can interfere with the endocrine system, potentially impacting hormone production and puberty timing. While research on the specific effects of endocrine disruptors on puberty is ongoing, concerns remain regarding their potential influence.
3. Socioeconomic Factors: Studies have shown that children from lower socioeconomic backgrounds tend to experience earlier puberty onset. This could be attributed to factors like nutritional deficiencies, stress, and exposure to environmental toxins, all of which can influence hormonal pathways.
4. Genetics and Family History: While not the primary driver of secular trends, genetic predisposition can play a role in the timing of puberty. Families with a history of early puberty may have a higher likelihood of their children also experiencing early onset.
5. Geographic Location and Climate: Variations in climate, sunlight exposure, and geographic location can influence puberty onset. Studies have shown that children living in warmer climates tend to experience earlier puberty compared to those living in colder climates.
Implications of Secular Trends in Puberty
The implications of secular trends in puberty are multifaceted and extend beyond the immediate physiological changes. These trends have potential implications for:
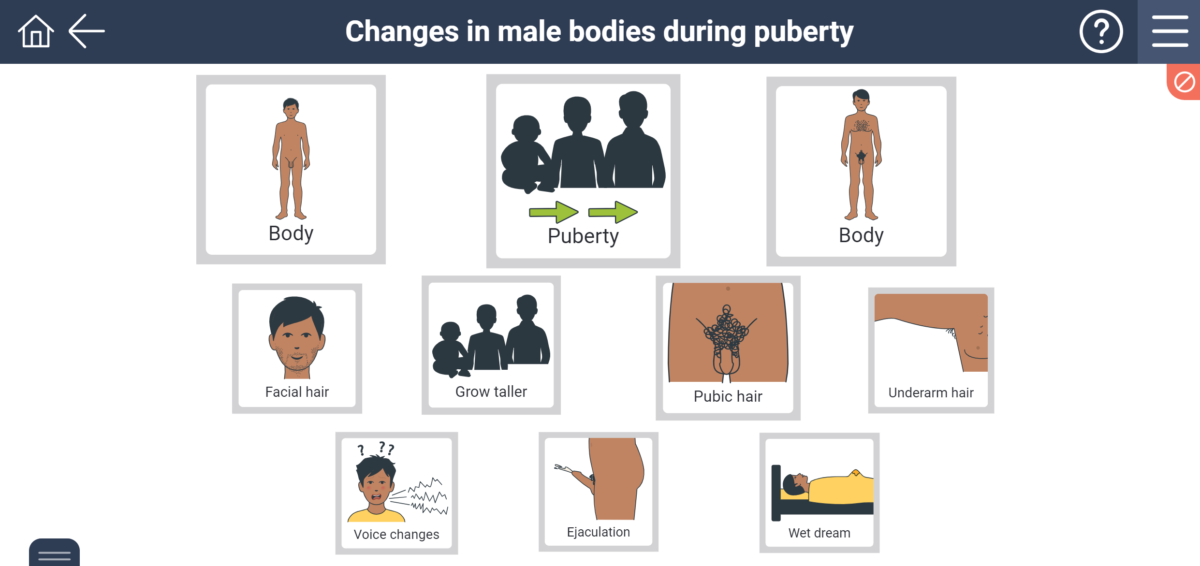
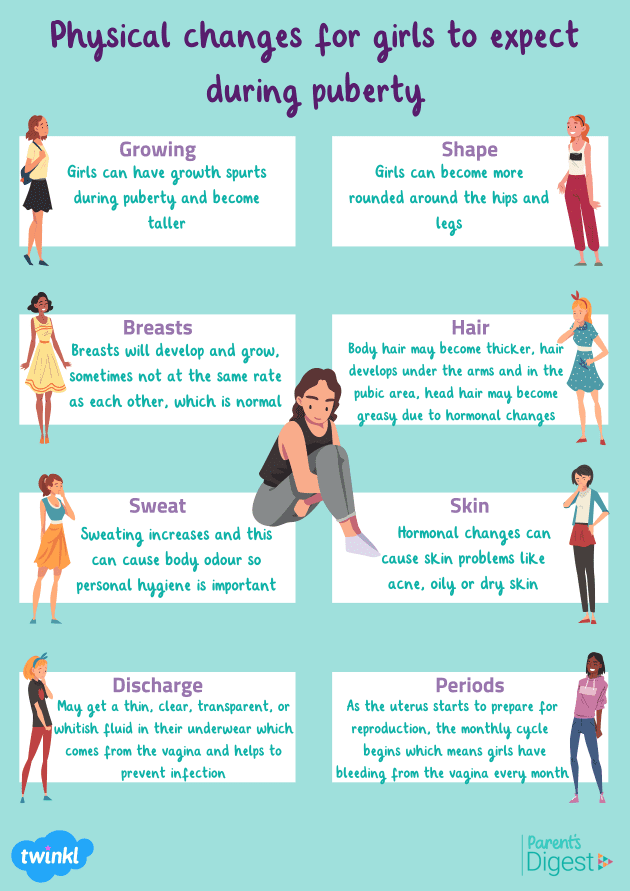
1. Physical Health: Early puberty onset in girls has been linked to an increased risk of developing certain health issues later in life, including breast cancer, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic disorders. Additionally, early puberty in boys may be associated with behavioral problems and substance abuse.
2. Mental Health: The emotional and social challenges of puberty can be amplified by early onset, particularly for girls who may experience social and emotional pressures associated with physical maturation at a younger age.
3. Social and Cultural Norms: The changing landscape of puberty raises questions about societal expectations and norms related to adolescence. As puberty occurs earlier, societal expectations and norms regarding sexual maturity and behavior need to be reevaluated.
4. Educational and Developmental Considerations: Early puberty onset can impact academic performance and social development. Children experiencing puberty at a younger age may face challenges in adjusting to the physical and emotional changes while simultaneously navigating academic demands and social interactions.
Secular Trends in Puberty: A Look Ahead to 2025
Predicting the future trajectory of secular trends in puberty is a complex task. However, considering current trends and research, we can anticipate the following:
1. Continued Early Onset: Based on the current trends, it is likely that puberty onset will continue to occur earlier in both boys and girls, particularly in regions with high levels of urbanization and exposure to environmental factors that may influence puberty timing.
2. Greater Variability: While overall trends indicate earlier onset, individual variations in puberty timing are likely to increase. This variability will be influenced by a multitude of factors, including genetics, socioeconomic status, and lifestyle choices.
3. Increased Awareness and Research: The growing awareness of secular trends in puberty will likely lead to increased research efforts aimed at understanding the underlying mechanisms, identifying contributing factors, and developing strategies to address potential health implications.
4. Emphasis on Holistic Health: The understanding of puberty as a complex developmental process will shift towards a more holistic approach, focusing on the physical, emotional, and social aspects of this transition.
5. Personalized Approaches: Healthcare professionals will likely adopt more personalized approaches to managing puberty, taking into account individual factors and tailoring interventions accordingly.
Related Searches:
1. Early Puberty in Girls: This search focuses on the specific implications of early puberty onset in girls, including the increased risk of certain health conditions and the potential impact on mental and social well-being.
2. Puberty Onset Trends: This search explores the overall trends in puberty onset across different populations, examining geographical variations, socioeconomic factors, and temporal changes.
3. Environmental Factors Affecting Puberty: This search delves into the role of environmental factors, such as endocrine disruptors, nutrition, and socioeconomic conditions, in influencing puberty timing.
4. Endocrine Disruptors and Puberty: This search focuses on the potential impact of endocrine disruptors, chemicals that can interfere with hormone production, on the timing and progression of puberty.
5. Puberty and Mental Health: This search explores the relationship between puberty onset and mental health, examining the potential for early puberty to contribute to anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges.
6. Puberty and Social Development: This search examines the impact of puberty onset on social development, including the challenges of navigating social interactions, peer relationships, and the pressures associated with physical maturation.
7. Puberty and Education: This search focuses on the potential impact of puberty onset on academic performance and educational outcomes, considering the challenges of balancing physical and emotional changes with academic demands.
8. Puberty Management: This search explores various strategies for managing puberty, including providing education, support, and medical interventions tailored to individual needs and concerns.
FAQs:
Q: What are the most significant factors contributing to secular trends in puberty?
A: The most significant factors contributing to secular trends in puberty are likely a combination of environmental and lifestyle influences, including increased access to calorie-rich diets, exposure to endocrine disruptors, and socioeconomic factors.
Q: Is early puberty always a cause for concern?
A: While early puberty can be associated with certain health risks, it is not always a cause for concern. The impact of early puberty varies depending on individual factors, and many children experience early puberty without experiencing any negative consequences.
Q: What can be done to address the potential health implications of secular trends in puberty?
A: Addressing the potential health implications of secular trends in puberty requires a multi-pronged approach, including promoting healthy lifestyles, reducing exposure to endocrine disruptors, and providing comprehensive healthcare services that address the physical, emotional, and social aspects of puberty.
Q: What are the long-term implications of secular trends in puberty for society as a whole?
A: The long-term implications of secular trends in puberty for society are complex and multifaceted. These trends may necessitate adjustments to societal norms and expectations related to adolescence, as well as changes to educational and healthcare systems to better address the needs of children experiencing puberty at earlier ages.
Tips:
1. Encourage Healthy Lifestyles: Promote healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, and adequate sleep to support overall health and well-being during puberty.
2. Reduce Exposure to Endocrine Disruptors: Be mindful of potential sources of endocrine disruptors in everyday products and choose safer alternatives whenever possible.
3. Provide Comprehensive Education: Offer age-appropriate education about puberty, including physical, emotional, and social changes, to empower children and adolescents with knowledge and understanding.
4. Foster Open Communication: Encourage open communication between parents, children, and healthcare professionals to address concerns and provide support during puberty.
5. Promote Positive Body Image: Encourage positive self-image and body acceptance, emphasizing that physical changes during puberty are normal and natural.
6. Advocate for Policy Changes: Support policies that promote healthy environments and reduce exposure to harmful substances that may impact puberty timing.
7. Promote Research and Awareness: Encourage continued research into the causes and implications of secular trends in puberty to enhance our understanding and develop effective strategies for addressing potential challenges.
Conclusion:
Secular trends in puberty are a complex and evolving phenomenon with significant implications for individual health, social norms, and healthcare systems. While the precise mechanisms driving these trends are still under investigation, the evidence suggests that environmental and lifestyle factors play a crucial role. Recognizing and understanding these trends is essential for developing effective strategies to address potential health concerns, promote healthy development, and navigate the changing landscape of adolescence in the years to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Landscape of Puberty: Exploring Secular Trends in 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!