Trends in Data Science 2025: Shaping the Future of Insights and Innovation
Related Articles: Trends in Data Science 2025: Shaping the Future of Insights and Innovation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Trends in Data Science 2025: Shaping the Future of Insights and Innovation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Trends in Data Science 2025: Shaping the Future of Insights and Innovation
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Trends in Data Science 2025: Shaping the Future of Insights and Innovation
- 3.1 1. The Rise of Explainable AI (XAI)
- 3.2 2. The Democratization of Data Science
- 3.3 3. The Integration of Data Science with Cloud Computing
- 3.4 4. The Rise of Edge Computing and the Internet of Things (IoT)
- 3.5 5. The Importance of Data Privacy and Security
- 3.6 6. The Growing Importance of Data Ethics
- 3.7 7. The Power of Data Storytelling
- 3.8 8. The Integration of Data Science with Other Disciplines
- 4 Related Searches
- 5 FAQs about Trends in Data Science 2025
- 6 Tips for Data Science Professionals in 2025
- 7 Conclusion: The Future of Data Science
- 8 Closure
Trends in Data Science 2025: Shaping the Future of Insights and Innovation
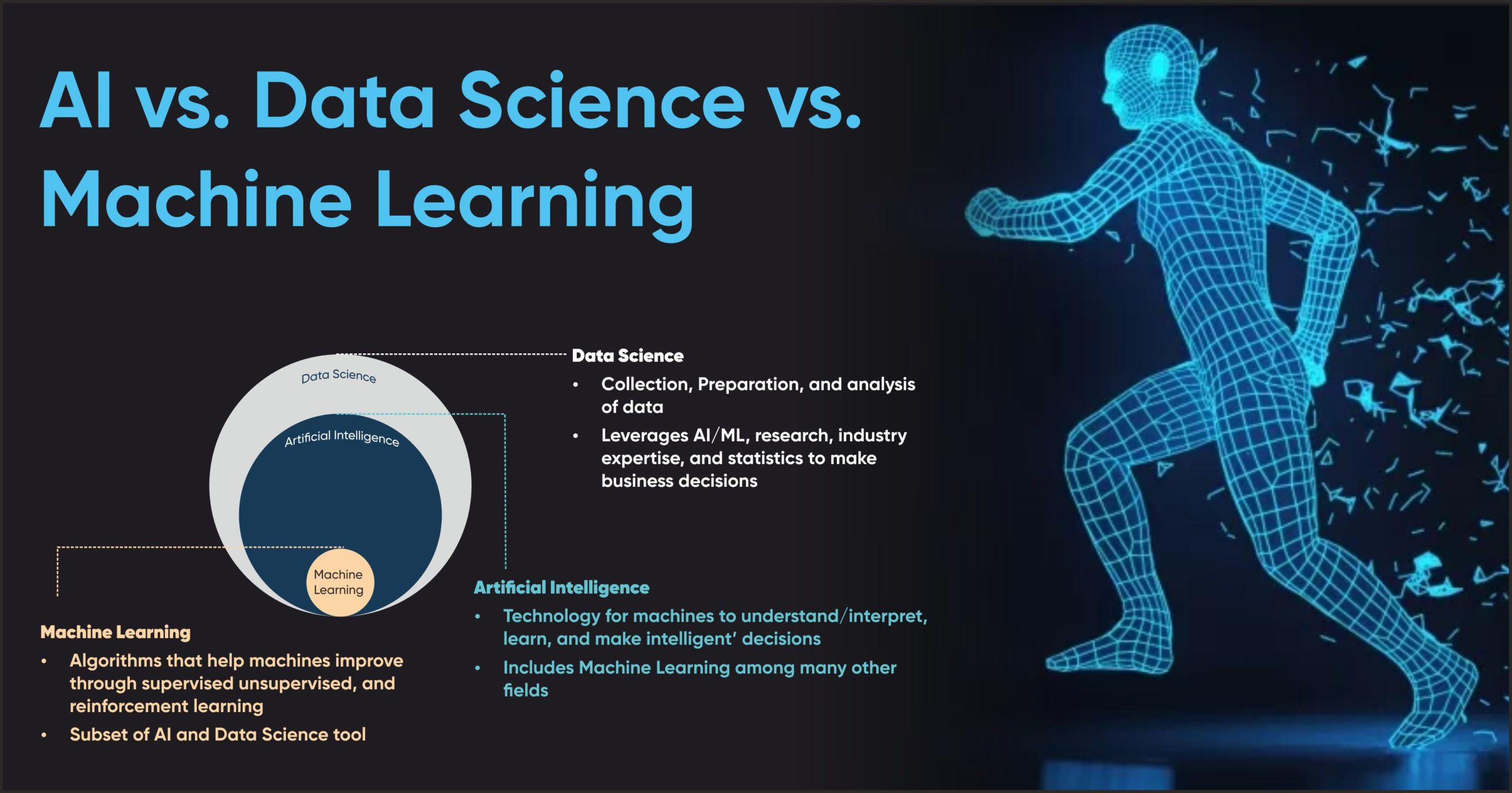
The field of data science is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, growing data volumes, and a rising demand for actionable insights. As we approach 2025, several key trends are poised to reshape the landscape of data science, influencing how businesses operate, researchers innovate, and individuals interact with the world around them.
Understanding the Importance of Data Science Trends
Staying abreast of these trends is crucial for individuals and organizations alike. For professionals, it means adapting skillsets, embracing new technologies, and staying competitive in a dynamic job market. For businesses, it signifies the potential to gain a competitive edge by leveraging data-driven insights to optimize operations, personalize customer experiences, and develop groundbreaking products and services.
Exploring the Key Trends Shaping Data Science in 2025
Here are eight key trends that will define the future of data science:
1. The Rise of Explainable AI (XAI)
As AI algorithms become increasingly complex, understanding their decision-making processes becomes paramount. Explainable AI (XAI) addresses this challenge by providing transparent and interpretable insights into AI models. This trend is crucial for building trust in AI systems, ensuring ethical use, and facilitating regulatory compliance.
Benefits of XAI:
- Improved Transparency: XAI helps users understand the reasoning behind AI decisions, enhancing trust and accountability.
- Enhanced Explainability: By providing clear explanations, XAI makes AI models more accessible and understandable to a wider audience.
- Ethical Considerations: XAI promotes fairness and unbiased decision-making, addressing concerns around algorithmic bias.
- Regulatory Compliance: As regulations surrounding AI usage evolve, XAI helps organizations comply with transparency requirements.
Examples of XAI in Action:
- Healthcare: XAI can help doctors understand the reasoning behind AI-powered diagnoses, facilitating informed decisions and improving patient care.
- Finance: XAI can provide transparent explanations for loan approvals or risk assessments, promoting fairness and trust in financial institutions.
- Legal: XAI can assist lawyers in understanding the reasoning behind legal decisions made by AI systems, ensuring transparency and accountability.
2. The Democratization of Data Science
Democratization of data science aims to make data science tools and techniques accessible to a broader audience, beyond traditional data scientists. This involves developing user-friendly platforms, simplifying complex algorithms, and promoting data literacy across various disciplines.
Benefits of Data Science Democratization:
- Increased Accessibility: More individuals can leverage data science tools and techniques, regardless of their technical background.
- Enhanced Innovation: By empowering a wider range of users, data science democratization fosters innovation and problem-solving across various industries.
- Improved Data Literacy: The democratization process encourages greater data literacy, enabling informed decision-making based on data-driven insights.
Examples of Data Science Democratization:
- Citizen Data Scientists: Individuals with limited technical backgrounds can utilize user-friendly data science platforms to analyze data and gain insights.
- Automated Machine Learning (AutoML): Tools that automate machine learning tasks, allowing users to build models without extensive coding knowledge.
- Data Visualization Tools: Easy-to-use platforms that enable users to create insightful visualizations from complex datasets.
3. The Integration of Data Science with Cloud Computing
Cloud computing plays a pivotal role in enabling data science initiatives by providing scalable infrastructure, powerful computing resources, and advanced data storage solutions. This integration empowers organizations to handle massive datasets, train sophisticated models, and deploy data science applications with ease.
Benefits of Cloud Integration:
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud computing offers on-demand resources, allowing organizations to scale their data science infrastructure as needed.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud services provide a pay-as-you-go model, reducing the need for upfront investments in hardware and software.
- Enhanced Security: Cloud providers offer robust security measures, ensuring data protection and compliance with industry standards.
Examples of Cloud Integration in Data Science:
- Cloud-Based Machine Learning Platforms: Services like Amazon SageMaker, Google Cloud AI Platform, and Microsoft Azure Machine Learning provide a platform for building and deploying machine learning models in the cloud.
- Cloud Data Warehouses: Services like Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, and Snowflake offer scalable data storage and analysis capabilities.
- Cloud-Based Data Visualization Tools: Platforms like Tableau and Power BI can be deployed on cloud infrastructure for collaborative data exploration and visualization.
4. The Rise of Edge Computing and the Internet of Things (IoT)
Edge computing and the Internet of Things (IoT) are transforming data science by bringing computation and data analysis closer to the source of data generation. This enables real-time insights and decision-making, reducing latency and improving responsiveness in applications like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial automation.
Benefits of Edge Computing and IoT:
- Real-Time Insights: Edge computing enables near-instantaneous data analysis, facilitating real-time decision-making and control.
- Reduced Latency: By processing data locally, edge computing minimizes the time required to transmit data to centralized servers, improving response times.
- Increased Efficiency: Edge computing optimizes resource utilization by processing data locally, reducing the load on centralized servers.
Examples of Edge Computing and IoT in Data Science:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Edge computing enables real-time analysis of sensor data for navigation, obstacle detection, and autonomous driving decisions.
- Smart Cities: Edge computing powers smart traffic management systems, environmental monitoring, and other applications that require real-time insights.
- Industrial Automation: Edge computing enables predictive maintenance, quality control, and other applications that optimize industrial processes.
5. The Importance of Data Privacy and Security
As data volumes continue to grow, data privacy and security become increasingly crucial. Data science professionals must adhere to strict regulations like GDPR and CCPA, ensuring data protection, responsible data usage, and ethical data handling practices.
Benefits of Data Privacy and Security:
- Trust and Reputation: Secure data handling practices build trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to data privacy regulations minimizes legal risks and penalties.
- Data Integrity: Robust security measures protect data from unauthorized access, ensuring its integrity and reliability.
Examples of Data Privacy and Security in Data Science:
- Data Anonymization and Pseudonymization: Techniques that protect sensitive information by removing identifying details.
- Differential Privacy: Methods that add noise to data to preserve privacy while enabling statistical analysis.
- Data Encryption: Secure storage and transmission of data using encryption algorithms to protect against unauthorized access.
6. The Growing Importance of Data Ethics
Data ethics is becoming increasingly important as data science applications impact society in profound ways. Data scientists must consider the ethical implications of their work, ensuring fairness, accountability, and responsible data usage.
Benefits of Data Ethics:
- Fair and Equitable Outcomes: Ethical data practices promote fairness and unbiased decision-making in AI systems.
- Transparency and Accountability: Data ethics emphasizes transparency in data collection, usage, and decision-making processes.
- Social Responsibility: Data scientists have a responsibility to use their skills ethically, considering the potential impact on society.
Examples of Data Ethics in Data Science:
- Algorithmic Bias Detection and Mitigation: Identifying and addressing bias in AI algorithms to ensure fair and equitable outcomes.
- Data Privacy and Consent: Ensuring that data is collected and used ethically and with informed consent.
- Responsible AI Development: Promoting ethical considerations throughout the AI development lifecycle, from data collection to model deployment.
7. The Power of Data Storytelling
Data storytelling involves transforming raw data into compelling narratives that engage audiences and drive action. This trend emphasizes the importance of communicating data insights effectively, using visualizations, narratives, and interactive presentations to convey complex information clearly and persuasively.
Benefits of Data Storytelling:
- Increased Engagement: Data storytelling captures attention and makes data insights more accessible and memorable.
- Improved Decision-Making: By presenting data in a compelling narrative, data storytelling facilitates informed and impactful decision-making.
- Enhanced Communication: Data storytelling bridges the gap between technical data analysis and business understanding, fostering effective communication.
Examples of Data Storytelling:
- Interactive Dashboards: Data visualizations that allow users to explore data interactively and uncover insights.
- Data-Driven Narratives: Stories that use data to support key points and illustrate trends.
- Infographics and Visualizations: Engaging visual representations of data that convey complex information in a concise and impactful manner.
8. The Integration of Data Science with Other Disciplines
Data science is no longer a standalone field. It is increasingly integrated with other disciplines, such as business intelligence, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and domain expertise. This interdisciplinary approach allows organizations to leverage data insights across various functions, driving innovation and achieving strategic goals.
Benefits of Interdisciplinary Integration:
- Holistic Insights: Combining data science with other disciplines provides a more comprehensive understanding of complex problems.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Interdisciplinary teams can work together to develop innovative solutions and address complex challenges.
- Improved Decision-Making: Integrating data science with other fields enables more informed and data-driven decision-making.
Examples of Interdisciplinary Integration:
- Business Intelligence and Data Science: Combining data analysis techniques with business intelligence tools to gain actionable insights and drive business growth.
- Machine Learning and Domain Expertise: Combining machine learning algorithms with domain expertise to develop tailored solutions for specific industries.
- Artificial Intelligence and Human-Computer Interaction: Integrating AI with human-computer interaction principles to create user-friendly and intuitive AI systems.
Related Searches
Here are some related searches that provide further insight into the trends shaping data science in 2025:
- Data Science Career Paths: Explore the various career paths available in data science, including data scientist, data analyst, machine learning engineer, and data architect.
- Data Science Skills: Identify the essential skills required for a successful career in data science, such as programming languages, statistical analysis, machine learning, and data visualization.
- Data Science Tools and Technologies: Discover the popular tools and technologies used in data science, including Python, R, SQL, Hadoop, Spark, TensorFlow, and PyTorch.
- Data Science Applications: Explore the diverse applications of data science across various industries, such as healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, and transportation.
- Data Science Education: Find resources for learning data science, including online courses, bootcamps, and university programs.
- Data Science Research: Stay up-to-date with the latest research in data science, including advancements in machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing.
- Data Science Ethics and Privacy: Understand the ethical considerations and privacy implications of data science applications.
- Data Science Trends in Specific Industries: Explore the specific trends in data science for different industries, such as healthcare, finance, and retail.
FAQs about Trends in Data Science 2025
Q1: What are the most important skills for data scientists in 2025?
Data scientists in 2025 will need a blend of technical and soft skills. Technical skills will include proficiency in programming languages like Python and R, statistical analysis, machine learning, and data visualization. Soft skills such as communication, collaboration, problem-solving, and critical thinking will be equally crucial for effectively communicating insights and working within interdisciplinary teams.
Q2: How will data science impact my career in the future?
Data science is rapidly transforming various industries. Regardless of your current career path, understanding data science principles and developing relevant skills will be increasingly valuable. Data science skills are highly sought after across diverse fields, enabling individuals to pursue exciting career opportunities and contribute to innovative solutions.
Q3: What are the biggest challenges facing data science in 2025?
Challenges facing data science include addressing ethical concerns around data usage, ensuring data privacy and security, mitigating algorithmic bias, and bridging the gap between technical expertise and business understanding. Addressing these challenges will be critical for responsible and impactful data science applications.
Q4: How can I stay ahead of the curve in data science?
Staying ahead of the curve requires continuous learning and adaptation. Engage in ongoing professional development, explore new technologies, attend conferences and workshops, and actively participate in online communities. Staying informed about emerging trends and advancements in data science will keep you competitive and adaptable in this dynamic field.
Tips for Data Science Professionals in 2025
- Embrace Continuous Learning: Data science is a rapidly evolving field. Dedicate time to ongoing professional development, exploring new technologies, and expanding your knowledge base.
- Develop Strong Communication Skills: Effectively communicating complex data insights to diverse audiences is crucial. Focus on developing your storytelling abilities, data visualization skills, and presentation techniques.
- Cultivate Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Collaborate with professionals from other disciplines, such as business analysts, domain experts, and software engineers, to leverage diverse perspectives and drive innovation.
- Stay Informed about Ethical Considerations: Understand the ethical implications of data science and prioritize responsible data usage, privacy protection, and algorithmic fairness.
- Embrace Automation and Tools: Leverage automation tools and platforms to streamline data analysis tasks, freeing up time for more strategic and creative work.
Conclusion: The Future of Data Science
The trends shaping data science in 2025 point towards a future where data-driven insights drive innovation, shape decision-making, and influence the way we interact with the world. By understanding these trends, individuals and organizations can prepare for the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead. The future of data science is bright, promising advancements in various fields and the potential to address some of society’s most pressing challenges. As we navigate this evolving landscape, the importance of ethical considerations, continuous learning, and collaboration will be paramount in ensuring that data science is used for good, driving positive change and shaping a better future.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Trends in Data Science 2025: Shaping the Future of Insights and Innovation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!