Unveiling the Secrets of the Periodic Table: A Look at Chemistry’s Enduring Trends in 2025
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Periodic Table: A Look at Chemistry’s Enduring Trends in 2025
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the Periodic Table: A Look at Chemistry’s Enduring Trends in 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Periodic Table: A Look at Chemistry’s Enduring Trends in 2025
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Secrets of the Periodic Table: A Look at Chemistry’s Enduring Trends in 2025
- 3.1 The Foundation of Periodic Trends: A Journey Through Atomic Structure
- 3.2 Applications of Periodic Trends: Shaping the Future of Chemistry
- 3.3 Exploring Related Searches: Delving Deeper into Periodic Trends
- 3.4 FAQs: Unraveling Common Questions about Periodic Trends
- 3.5 Tips: Mastering Periodic Trends
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Periodic Trends
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Secrets of the Periodic Table: A Look at Chemistry’s Enduring Trends in 2025
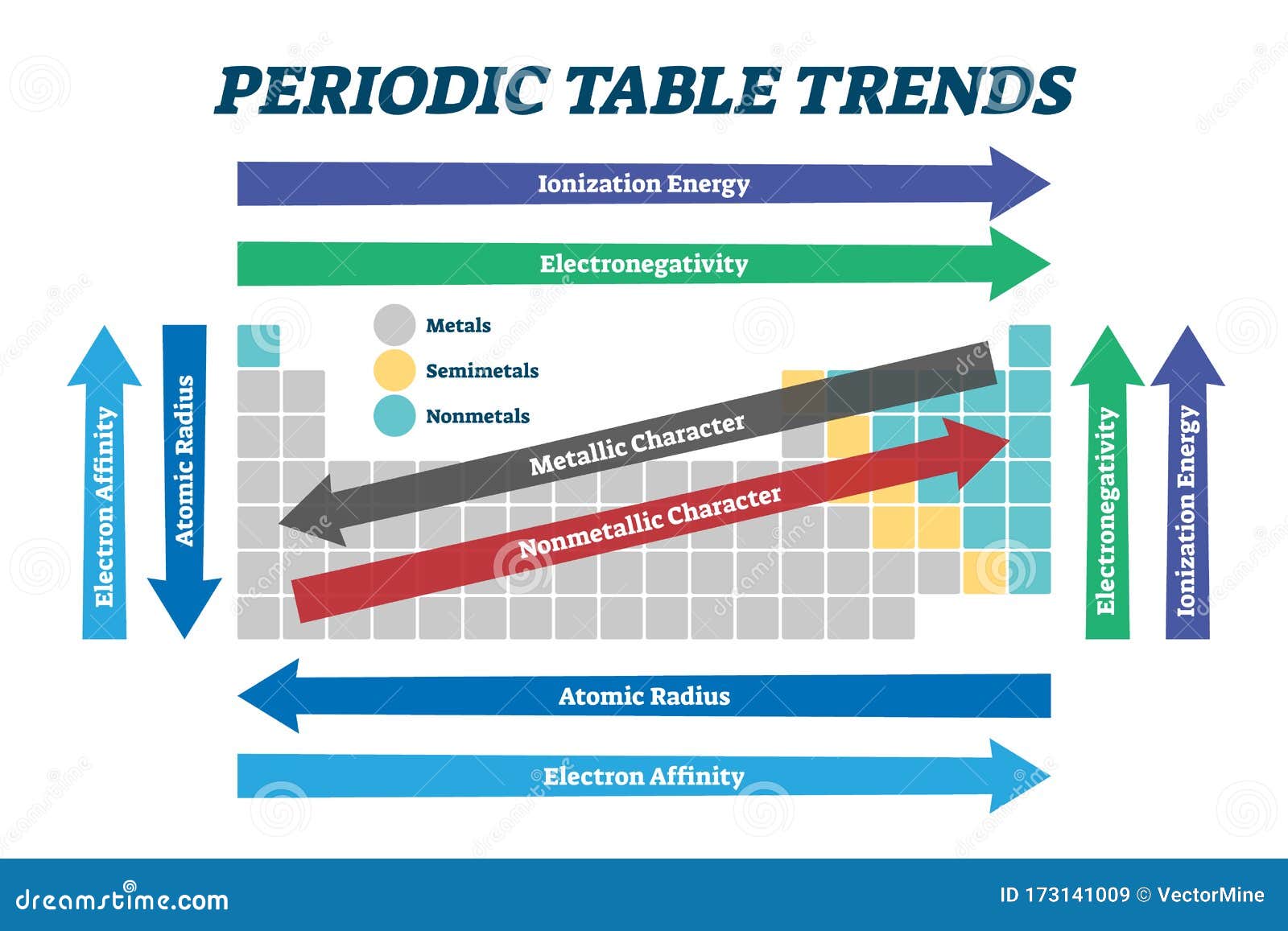
The periodic table, a cornerstone of chemistry, is a testament to the elegance and order of the natural world. It organizes the elements, not merely in a list, but in a structure that reveals profound relationships and predictable patterns. These patterns, known as periodic trends, are the guiding principles that govern the behavior of elements and dictate their interactions.
Understanding periodic trends is crucial for comprehending the vast landscape of chemistry. They empower us to predict the properties of elements, design new materials, and unravel the mysteries of chemical reactions. As we stand on the precipice of 2025, the study of periodic trends remains as vital as ever, driving innovation in diverse fields like medicine, energy, and technology.
The Foundation of Periodic Trends: A Journey Through Atomic Structure
The heart of periodic trends lies in the atomic structure of elements. As we move across a period or down a group in the periodic table, the arrangement of electrons within an atom changes systematically, giving rise to observable trends in properties.
-
Electronegativity: This measures an atom’s tendency to attract electrons in a chemical bond. Moving across a period, electronegativity increases due to a stronger pull from the nucleus as the number of protons increases. Conversely, moving down a group, electronegativity decreases as the outermost electrons are farther from the nucleus and less attracted to it.
-
Ionization Energy: This is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom. Ionization energy generally increases across a period due to the stronger attraction between the nucleus and electrons. Down a group, ionization energy decreases as the outer electrons are further away from the nucleus and easier to remove.
-
Electron Affinity: This describes the change in energy when an electron is added to a neutral atom in the gaseous state. Electron affinity generally increases across a period, with the exception of some elements like nitrogen and oxygen. Moving down a group, electron affinity decreases as the added electron experiences weaker attraction from the nucleus.
-
Atomic Radius: This refers to the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron shell of an atom. Atomic radius decreases across a period as the increasing nuclear charge pulls the electrons closer. Conversely, it increases down a group as the number of electron shells increases.
-
Metallic Character: This refers to the tendency of an element to lose electrons and form positive ions. Metallic character increases down a group as the outer electrons are further from the nucleus and easier to lose. Across a period, metallic character generally decreases as the attraction between the nucleus and electrons strengthens.
These trends, intricately woven together, provide a comprehensive understanding of how elements behave and interact. They are the key to deciphering the intricate dance of atoms and molecules, guiding us towards a deeper understanding of the chemical world.
Applications of Periodic Trends: Shaping the Future of Chemistry
Periodic trends are not mere theoretical concepts; they are the driving force behind countless advancements in science and technology. Their practical applications extend far beyond the confines of the laboratory, touching every facet of our lives.
-
Material Science: Understanding periodic trends is crucial for designing new materials with tailored properties. For instance, the increasing electronegativity across a period allows us to create materials with enhanced electrical conductivity or improved thermal stability.
-
Drug Development: In pharmaceutical research, periodic trends play a critical role in identifying potential drug candidates. By understanding the electron affinity and ionization energy of elements, scientists can predict how molecules will interact with biological targets, leading to the development of more effective and targeted therapies.
-
Energy Production: The quest for clean and sustainable energy sources relies heavily on periodic trends. Understanding the properties of elements like lithium and silicon is essential for developing advanced battery technologies and efficient solar cells.
-
Environmental Science: periodic trends are indispensable for understanding environmental pollution and finding solutions to mitigate its impact. By analyzing the behavior of elements like mercury and lead, we can develop strategies for reducing their release into the environment and mitigating their harmful effects.
-
Catalysis: Catalysts, essential for many chemical processes, are often designed based on periodic trends. Understanding the reactivity and selectivity of different elements allows us to create catalysts that accelerate specific reactions, improving efficiency and minimizing waste.
Exploring Related Searches: Delving Deeper into Periodic Trends
The vastness of periodic trends extends beyond the core principles. Numerous related searches offer deeper insights into specific aspects of this fundamental concept.
1. Periodic Trends and Chemical Bonding:
- Ionic Bonding: This type of bonding arises from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. Understanding the electronegativity of elements is key to predicting the formation of ionic bonds.
- Covalent Bonding: This involves the sharing of electrons between atoms. The electronegativity difference between atoms determines the type of covalent bond formed, ranging from purely covalent to polar covalent.
- Metallic Bonding: This type of bonding occurs in metals, where electrons are delocalized throughout the entire structure, leading to high electrical conductivity and malleability.
2. Periodic Trends and Chemical Reactions:
- Reactivity: The tendency of an element to participate in chemical reactions is influenced by its ionization energy and electron affinity. Elements with low ionization energy and high electron affinity tend to be more reactive.
- Oxidation States: The oxidation state of an element reflects its ability to gain or lose electrons in a reaction. Understanding the periodic trends in electronegativity helps predict the oxidation states of elements in different compounds.
- Redox Reactions: These reactions involve the transfer of electrons. The reactivity of elements in redox reactions is directly related to their ionization energy and electron affinity.
3. Periodic Trends and Physical Properties:
- Melting Point and Boiling Point: These properties are influenced by the strength of interatomic forces. Elements with strong metallic bonding tend to have high melting and boiling points.
- Density: The density of an element is determined by its atomic mass and atomic radius. Elements with high atomic mass and small atomic radius tend to have high density.
- Color: The color of an element is determined by its electronic configuration and the way it absorbs and emits light. Elements with specific electronic configurations often exhibit characteristic colors.
4. Periodic Trends and Applications in Technology:
- Semiconductors: The properties of semiconductors, essential for electronics, are directly related to their electronic configuration and band structure. Understanding periodic trends allows for the design of semiconductors with specific properties.
- Superconductors: These materials exhibit zero electrical resistance at low temperatures. The search for new superconductors relies heavily on understanding the relationship between atomic structure and superconducting properties.
- Nanotechnology: At the nanoscale, the properties of materials can change drastically. Understanding periodic trends is crucial for designing nanomaterials with specific properties for applications in medicine, energy, and electronics.
5. Periodic Trends and Environmental Issues:
- Pollution: Understanding the properties of elements like mercury, lead, and arsenic is crucial for addressing environmental pollution. Periodic trends help us understand their behavior in the environment and develop strategies for remediation.
- Climate Change: The impact of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane is directly related to the properties of these molecules. Understanding periodic trends is essential for developing strategies to mitigate climate change.
- Resource Management: The scarcity of certain elements, like rare earth metals, poses challenges for sustainable resource management. periodic trends can help us identify alternative materials and develop efficient recycling methods.
6. Periodic Trends and the Future of Chemistry:
- New Elements: The periodic table is not static; new elements are continuously being discovered. Understanding periodic trends is crucial for predicting the properties of these new elements and exploring their potential applications.
- Computational Chemistry: Advancements in computational chemistry allow us to model and predict chemical behavior with unprecedented accuracy. Periodic trends play a critical role in developing and validating these computational models.
- Artificial Intelligence in Chemistry: AI is increasingly being used to analyze and interpret chemical data. Understanding periodic trends is essential for training AI algorithms to predict and optimize chemical reactions.
7. Periodic Trends and the History of Chemistry:
- Mendeleev’s Contribution: Dmitri Mendeleev, the father of the periodic table, recognized the importance of periodic trends and used them to predict the properties of undiscovered elements.
- The Development of Quantum Mechanics: The development of quantum mechanics provided a theoretical framework for understanding periodic trends and their underlying causes.
- The Evolution of the Periodic Table: The periodic table has evolved over time, with new elements being discovered and the understanding of periodic trends deepening.
8. Periodic Trends and Education:
- Teaching Chemistry: Periodic trends are a fundamental concept in chemistry education. Understanding these trends helps students develop a deeper understanding of chemical principles and apply them to real-world problems.
- Science Literacy: Periodic trends are essential for scientific literacy. They provide a framework for understanding the world around us and making informed decisions about scientific issues.
- Inspiring Future Scientists: The beauty and elegance of periodic trends can inspire young minds to pursue careers in science and contribute to the advancement of knowledge.
FAQs: Unraveling Common Questions about Periodic Trends
1. Why are periodic trends important?
Periodic trends are crucial for understanding the behavior of elements and predicting their interactions. They provide a framework for comprehending the vast landscape of chemistry and guide us towards developing new materials, technologies, and solutions to global challenges.
2. How do periodic trends relate to the atomic structure?
The arrangement of electrons within an atom, specifically the outermost electrons, dictates the trends observed in properties like electronegativity, ionization energy, and atomic radius.
3. What are some practical applications of periodic trends?
Periodic trends are essential for designing new materials, developing drugs, producing energy, understanding environmental issues, and advancing technology.
4. How can I learn more about periodic trends?
There are numerous resources available, including textbooks, online articles, and videos. You can also explore related searches to delve deeper into specific aspects of periodic trends.
5. What are some future directions for research in periodic trends?
Future research will focus on understanding the properties of new elements, developing computational models to predict chemical behavior, and utilizing AI to analyze and interpret chemical data.
Tips: Mastering Periodic Trends
- Visualize the Periodic Table: Use a periodic table as a visual aid to understand the relationships between elements and how properties change across periods and groups.
- Focus on the Key Trends: Concentrate on understanding the key trends like electronegativity, ionization energy, and atomic radius, as they provide a foundation for predicting other properties.
- Practice with Examples: Work through practice problems to solidify your understanding of periodic trends and apply them to real-world scenarios.
- Connect Trends to Applications: Relate periodic trends to their practical applications in fields like material science, drug development, and energy production.
- Explore Related Searches: Delve deeper into specific areas of periodic trends by exploring related searches and seeking out additional resources.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Periodic Trends
The periodic table, with its elegant organization and predictable patterns, serves as a testament to the order and beauty of the natural world. Periodic trends, the underlying principles that govern this order, continue to be a cornerstone of chemistry, guiding our understanding of the chemical world and driving innovation in various fields. As we move forward, the study of periodic trends will remain essential for unraveling the mysteries of the universe and shaping a brighter future for humanity.




/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the Periodic Table: A Look at Chemistry’s Enduring Trends in 2025. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!